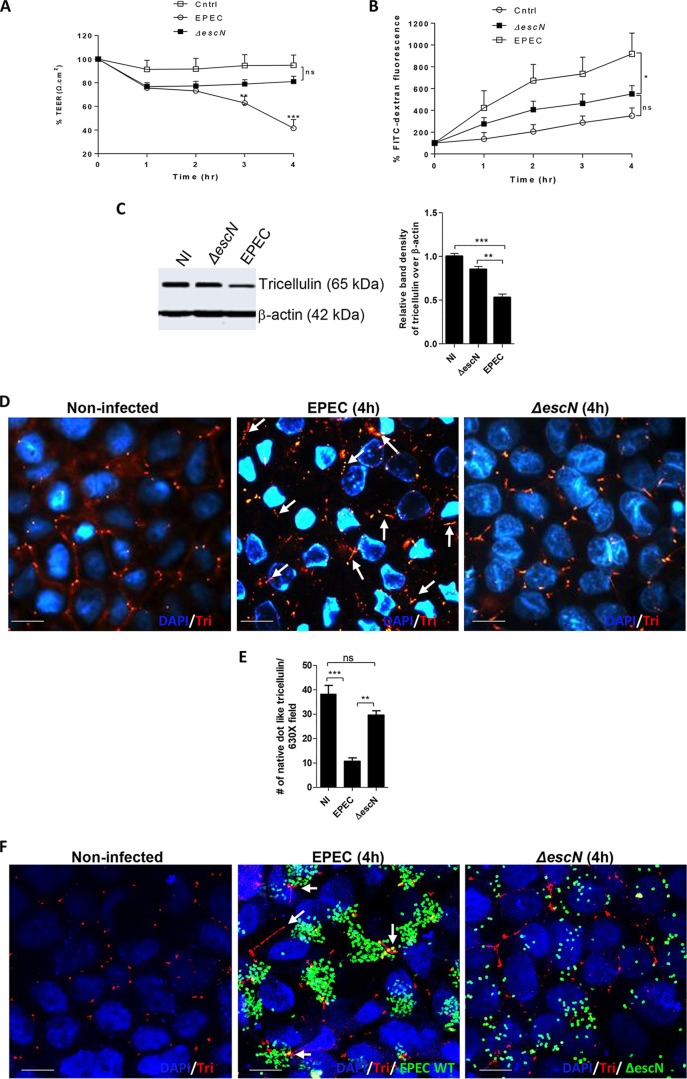
FIG 2.
Tricellulin expression and localization to tTJs are dependent on EPEC T3SS. (A and B) Caco-2 cells were infected with ΔescN mutant EPEC strains and measured for TEER (A) and FITC-dextran tracer fluorescence (B). The data are averages from >3 independent experiments with 3 wells per condition. Two independent experiments with 3 wells per condition were used for analysis. (C) Cell lysates obtained from control, ΔescN mutant, and WT EPEC strains were probed for the expression of tricellulin. (D) Tricellulin (Tri) detection by fluorescence microscopy in noninfected, ΔescN mutant-infected, and WT EPEC-infected cells. Magnifications, ×2,000. (E) Microscopic evaluation of the total number of native dot-like tricellulin structures localized at tTJs. For each strain, a minimum of 8 to 10 images from 3 independent experiments were analyzed at a magnification of ×630. (F) Confocal imaging of cells infected with GFP-labeled WT EPEC and ΔescN EPEC strains immunolabeled for tricellulin. Magnifications, ×2,000. For panels D and F, blue, nuclei; green, GFP-labeled EPEC; red, tricellulin. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001; ns, nonsignificant. Arrows, loss of native dot-like structure of tricellulin.