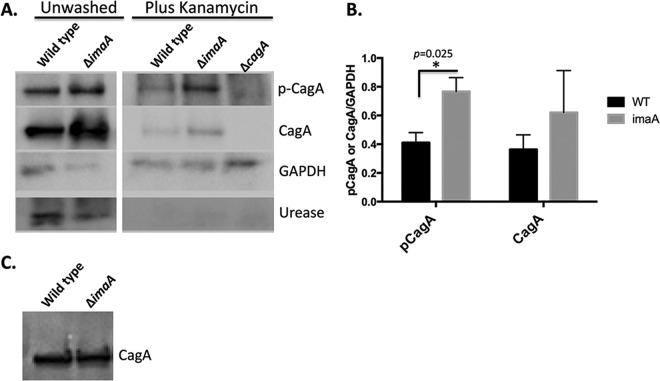
FIG 2.
imaA mutants deliver more CagA into epithelial cells. (A) AGS cells were infected with either wild-type H. pylori or the imaA mutant for 3 h until treatments were initiated as follows: (i) cells were unwashed, where AGS cells remained unwashed and the infection was allowed to persist for an additional 6 h, or (ii) cells were washed and treated with Km for 6 h, in which AGS cells were washed 3 times and supplemented with medium containing kanamycin for an additional 6 h. After the 6-h period, AGS cells were washed, collected, and analyzed by Western blotting with the antibodies indicated at the right of the blot. p-CagA, phosphorylated CagA. (B) CagA protein levels were quantified from 3 biological replicates using ImageJ pixel densitometry software. *, P < 0.05 by Student's t test. WT, wild type. (C) Lysates from wild-type H. pylori and the imaA mutant grown as described in the legend to panel A were examined for CagA production prior to AGS cell infection using Western blotting. Equal numbers of cells, based on the OD600, were loaded in each lane.