Fig. 6.
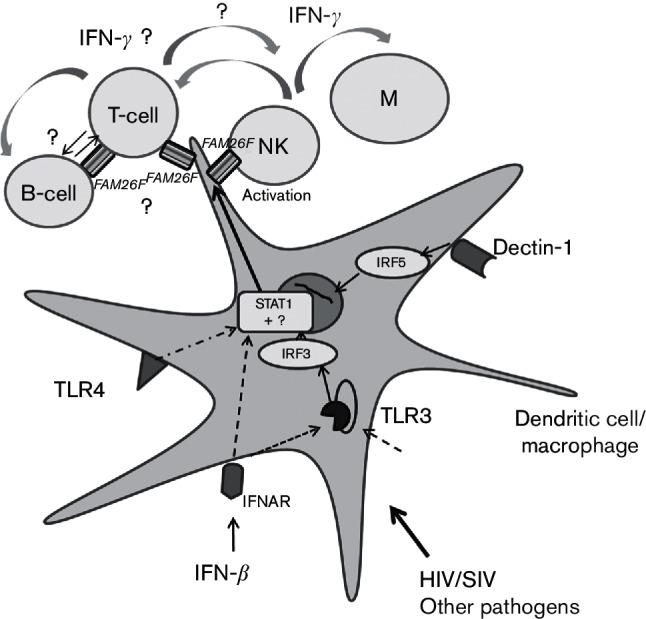
Schematic view illustrating current knowledge and hypothetical role of FAM26F in immune response induction. Activation of dendritic cells/macrophages via IFN-α/β receptor (IFNAR), TLR3, TLR4 and/or dectin-1 and pathogens results in increased FAM26F expression probably through activation of STAT1 (Chiba et al., 2014; Chmielewski et al., 2014; Ebihara et al., 2010; Kasamatsu et al., 2014; Lee et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2010). Deletion of IRF-3 or IRF-5 reduces FAM26F expression in mice (Chiba et al., 2014; Ebihara et al., 2010). Expression of FAM26F contributes to early IFN-γ secretion and tumour reduction by NK cells (Kasamatsu et al., 2014). The effect of FAM26F expression in T-cells, B-cells and other immune cells in terms of further augmentation of an IFN-γ response through FAM26F-mediated cell–cell contact is hypothetical and requires further investigation.
