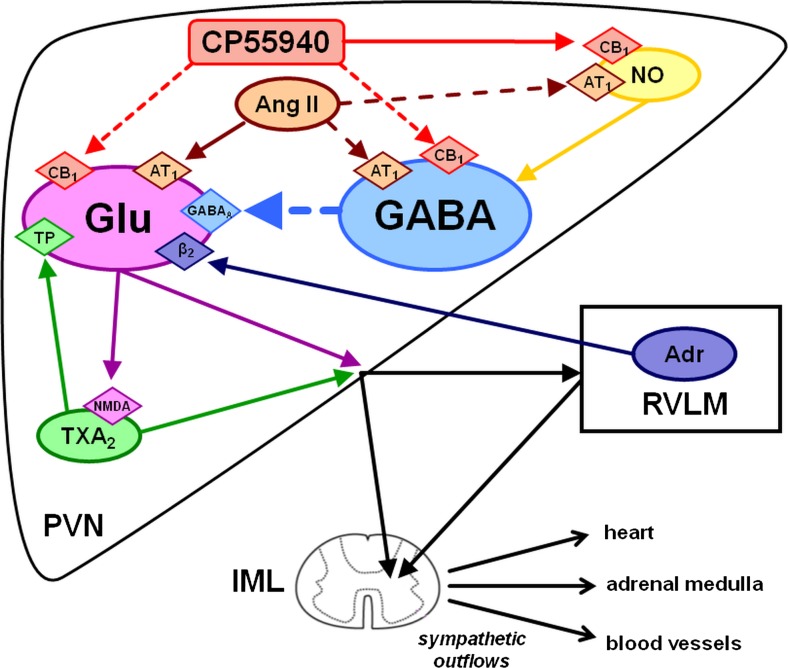
Fig. 5.
Possible mechanisms involved in the effect of the CB receptor agonist CP55940 topically administered to the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) on the sympathetic outflow and cardiovascular parameters. Activation of presynaptic inhibitory CB1 receptors on glutamatergic (Glu) neurones leads to a decrease in the sympathetic outflow (mainly to resistance vessels and heart) and a fall in blood pressure. Activation of presynaptic inhibitory CB1 receptors on GABAergic (γ-aminobutyric acid) neurons leads to an increase in the sympathetic outflow (mainly of the adrenal medulla) and in blood pressure. Activation of presynaptic facilitatory (i) angiotensin II (Ang II) AT1, (ii) thromboxane A2 (TXA2) TP and (iii) adrenaline (Adr) β2-adrenergic receptors increases whereas activation of GABAA receptors decreases the release of glutamate. Nitric oxide (NO) stimulates GABA release. For the sake of clarity, only interactions examined in the present study have been shown in this scheme. An inhibitory effect of Ang II and a facilitatory effect of CP55940 on NO production although opposite in direction to the effects usually obtained by AT1 and CB1 receptor activation, respectively, are also indicated.  stimulatory inputs;
stimulatory inputs;  inhibitory inputs. RVLM rostral ventrolateral medulla, IML intermediolateral column
inhibitory inputs. RVLM rostral ventrolateral medulla, IML intermediolateral column