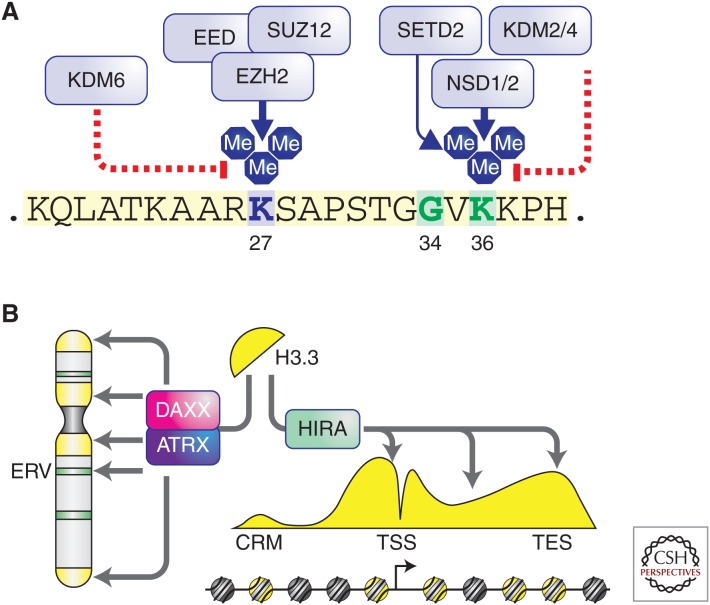
Figure 1.
Posttranslational modification of the histone variant H3.3 and its chaperone/deposition machinery. (A) The amino-terminal tail of histone H3.3 (shown here) and other histone H3 proteins are subject to methylation of lysine residue 27 by the Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), containing core subunits EED, SUZ12, and EZH2. Removal of H3K27 methylation is performed by KDM6 family demethylases, including JMJD3 and UTX. Lysine residue 36 is subject to methylation by multiple enzymes, including the NSD family enzymes and SETD2. Removal of H3K36 methylation is performed by the KDM2 and KDM4 family demethylases. (B) Histone variant H3.3 is deposited at pericentric heterochromatin, telomeres, and certain endogenous retroviral elements (ERV) by the ATRX/DAXX heterodimeric complex. In contrast, H3.3 is deposited at euchromatin regions such as promoters and gene bodies by the histone chaperone HIRA (see Banaszynski et al. 2010 and Maze et al. 2014 for details and references).