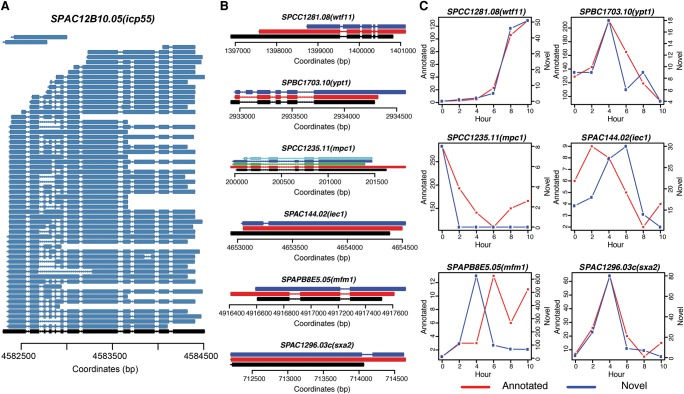
Figure 3.
Examples of alternative splicing during S. pombe meiosis. (A) Fifty-nine different isoforms were detected for SPAC12B10.05(icp55). Black represents the annotation and dark blue represents detected isoforms. Aligned nucleotides are denoted by solid lines and alignment gaps indicating introns are marked by thin lines with arrows indicating the strand. (B) Six different types of alternative splicing structures. SPCC1281.08(wtf11) (novel splicing donor or acceptor); SPBC1703.10(ypt1) (exon inclusion); SPCC1235.11(mpc1) (exon skipping); SPAC144.02(iec1) (intron in exon); SPAPB8E5.05(mfm1) (intron retention); SPAC1296.03c(sxa2) (novel exon). Black marks the annotated structure; red depicts isoforms that match the internal annotated structure; all other colors (dark blue, light blue, green) denote structurally different AS isoforms. (C) Dynamics of annotated isoform and novel isoform for each of the six examples shown in B. Red lines represent numbers of FL CCS reads for annotated isoforms and blue lines represent numbers of FL CCS reads for novel isoforms during meiosis.