Figure 1.
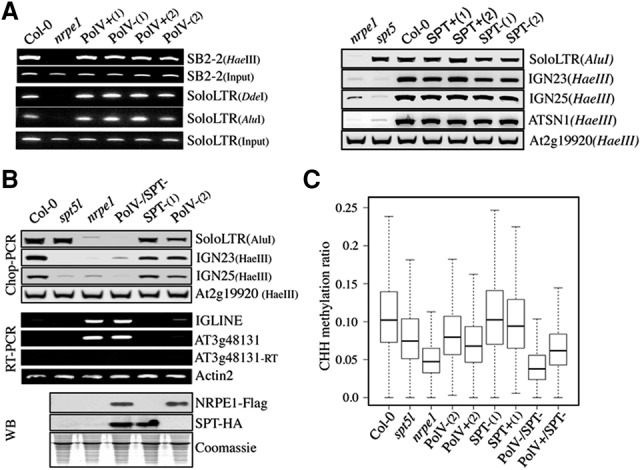
Pol V and SPT5L AGO hook motifs are functionally redundant and essential for RdDM. (A, left panel) Analysis of DNA methylation by Chop PCR at SB2-2 and soloLTR loci in Col-0, nrpe1, Pol V+(1,2), and Pol V−(1,2) lines. Genomic DNA digested with HaeIII, DdeI, and AluI methylation-sensitive enzymes was used as a template for PCR. Undigested DNA (input) was used as a control. (Right panel) Analysis of DNA methylation by Chop PCR at RdDM targets in nrpe1, spt5l, Col-0, SPT+(1,2), and truncated SPT−(1,2) lines. Genomic DNA digested with AluI and HaeIII methylation-sensitive enzymes was used as a template for PCR. The At2g19920 locus was used as a control. (B, top panel) Analysis of DNA methylation by Chop PCR at RdDM targets in Col-0, spt5l, nrpe1, Pol V−/SPT−, SPT−(1), and Pol V−(2) lines. Genomic DNA was digested with HaeIII and AluI methylation-sensitive enzymes. The At2g19920 locus was used as a control. (Middle panel) Transcript levels at two RdDM targets (IGLINE and AT3g48131) in Col-0, spt5l, nrpe1, Pol V−/SPT−, SPT−(1), and Pol V−(2) lines. ACTIN2 was used as a loading control, and −RT reactions show the absence of genomic DNA contamination. (Bottom panel) Detection of Pol V/NRPE1 and SPT variants by Western blot. Coomassie blue staining was used as a loading control. (C) Whole-genome bisulfite analysis of DNA methylation in Col-0, nrpe1, spt5l, Pol V−(2), Pol V+(2), SPT−(1), SPT+(1), Pol V−/SPT−, and Pol V+/SPT− lines. Box plots represent whole-genome CHH methylation ratios at regions previously identified as targeted by Pol V (Zhong et al. 2012). A dependent two-group Wilcoxon signed rank test was run on methylation at the Pol V sites for Pol V−/SPT− versus Pol V+/SPT− and revealed that there is a significant difference in methylation levels. P < 2.2 × 10−16.
