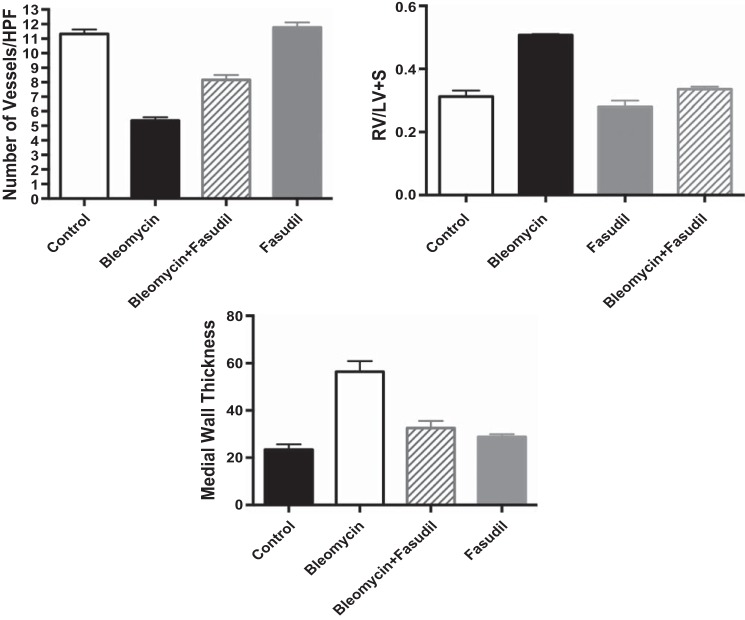
Fig. 7.
Effect of intraperitoneal bleomycin, alone or in combination with Rho kinase inhibition (fasudil) and nonselective ET blockade (bosentan), on vessel density, Fulton's index (RV/LV+S), and medial wall thickness (MWT) in neonatal rat pups. Compared with controls (n = 5), bleomycin treatment (n = 5) decreased vessel density by 53% (P < 0.01). Fasudil increased vessel density by 52% (P < 0.01) (n = 5 animals); however, compared with controls vessel density remained decreased by 28% (P < 0.05). This effect was similar to what was seen with bosentan, which increased vessel density by 56%. Treatment with fasudil and bosentan alone (n = 5 animals) had no effect on vessel density in neonatal rat pups and values remained similar to controls. Bleo increased MWT by 128% (P < 0.01). Treatment with fasudil decreased MWT 49% (P < 0.01), restoring MWT to control values. This effect was similar to what was seen with bosentan. Bleomycin treatment increased RV/LV+S by 63% (P < 0.01). Fasudil in combination with bleomycin decreased RV/LV+S by 34% (P < 0.01), restoring RV/LV+S to control values. This effect was similar to what was seen with bosentan, which decreased RV/LV+S by 36%. Treatment with fasudil and bosentan alone had no effect on MWT and RV/LV+S in neonatal rat pups, and values remained similar to controls.