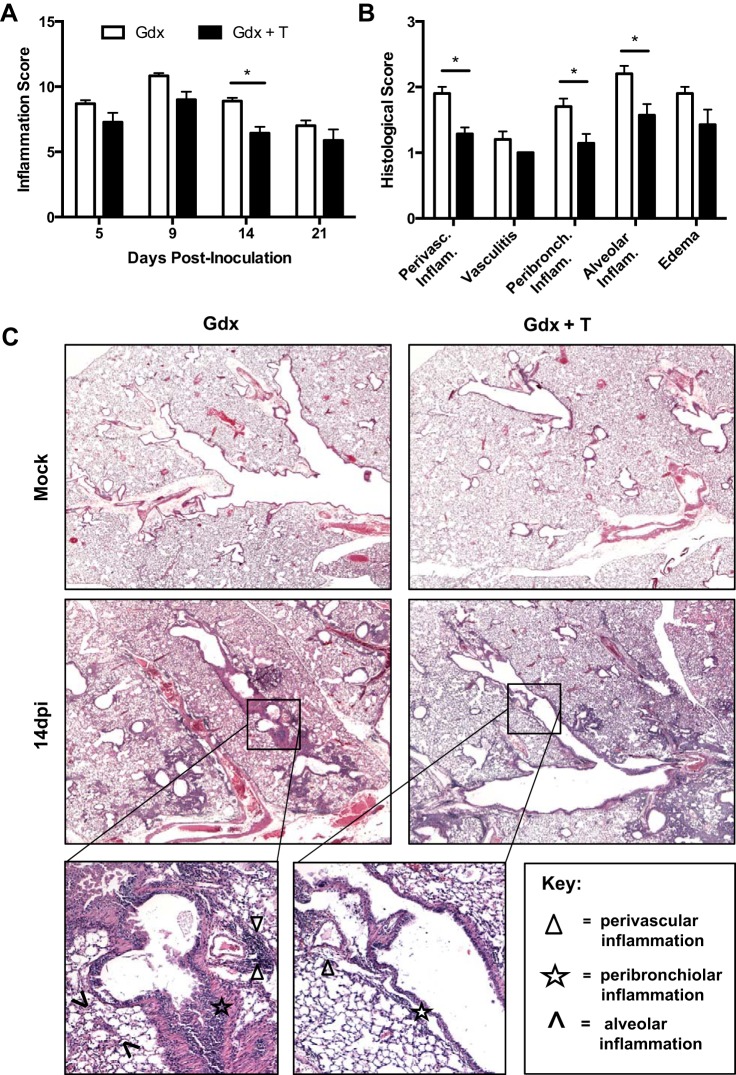
Fig. 5.
Effects of testosterone treatment on pulmonary inflammation following ma2009 virus infection in young adult males. Lungs were collected from young adult males that were gonadectomized and treated with either placebo (Gdx) or testosterone (Gdx + T) and either mock infected or infected with influenza A virus (ma2009) and euthanized at 5, 9, 14, or 21 days dpi (n = 6–10/treatment/time point). Lung tissues were sectioned, stained with H&E, and scored for makers of inflammation, including perivascular inflammation, peribronchiolar inflammation alveolar inflammation, and edema. A: cumulative inflammation scores at 5, 9, 14, or 21 dpi are presented. Histology scores (B) and representative photomicrographs (C) are shown for 14 dpi. *Significant difference between gonadectomized young adult male mice treated with placebo or testosterone (P < 0.05).