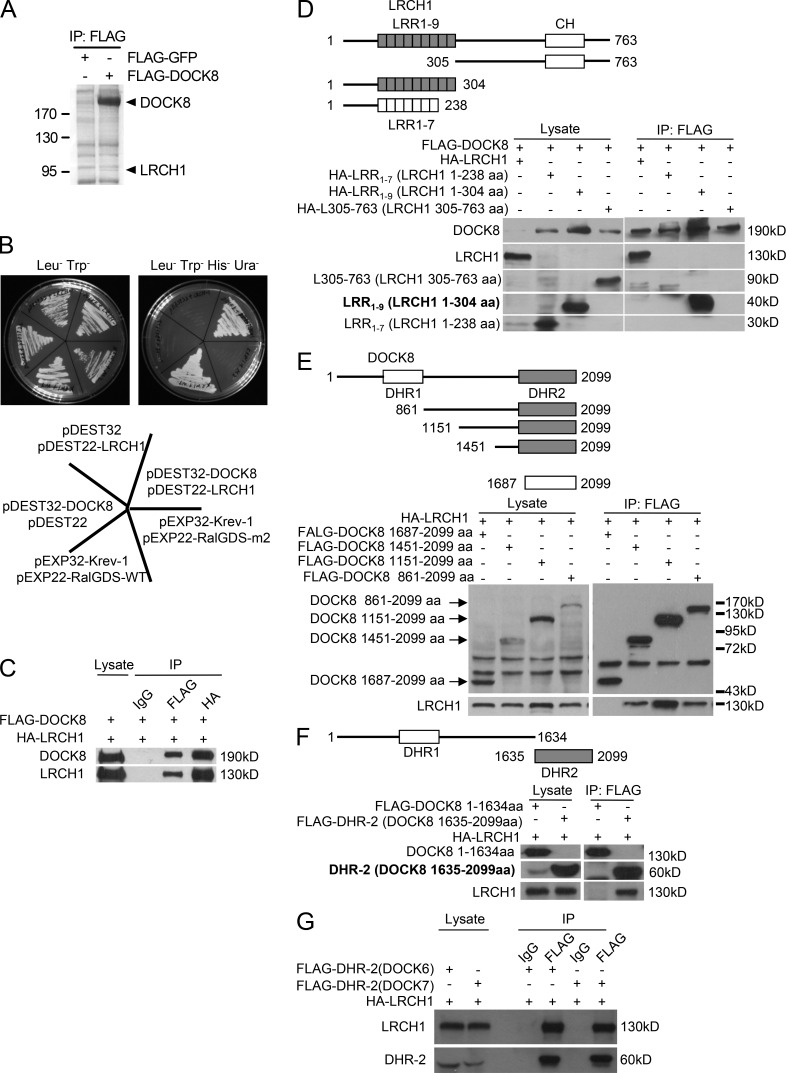
Figure 3.
Identification of LRCH1 as a new binding partner of DOCK8. (A) An anti-FLAG IP was performed with FLAG-DOCK8–transfected T8.1 cells for the mass spectrometry assay, and the Coomassie blue staining is shown. (B) DOCK8 interaction with LRCH1 in the yeast two-hybrid system. DOCK8 and the pDEST22 vector, LRCH1 and the pDEST32 vector, and DOCK8 and LRCH1 were cotransfected into the yeast strain Mav 203-activated expression of β-glycosidase. Krev-1 and RalGDS-WT were cotransfected as a positive control. Krev-1 and RalGDS-m2 were cotransfected as a negative control. (C–F) 293T cells were cotransfected with FLAG-DOCK8 and HA-LRCH1 (C); FLAG-DOCK8 and HA-LRCH1 or its deletion mutants (HA-LRCH1 1–238 aa, 1–304 aa, or 305–763 aa; D); HA-LRCH1 and FLAG-DOCK8 or its mutants (DOCK8 861–2099 aa, 1151-2099 aa, 1451-2099 aa, and 1687–2099 aa, or 1–1634 aa, 1635–2099 aa; E and F) for immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (G) 293T cells were cotransfected with HA-tagged LRCH1 and FLAG-tagged the DHR2 domain of DOCK6 or DOCK7. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Data are representative of three experiments.