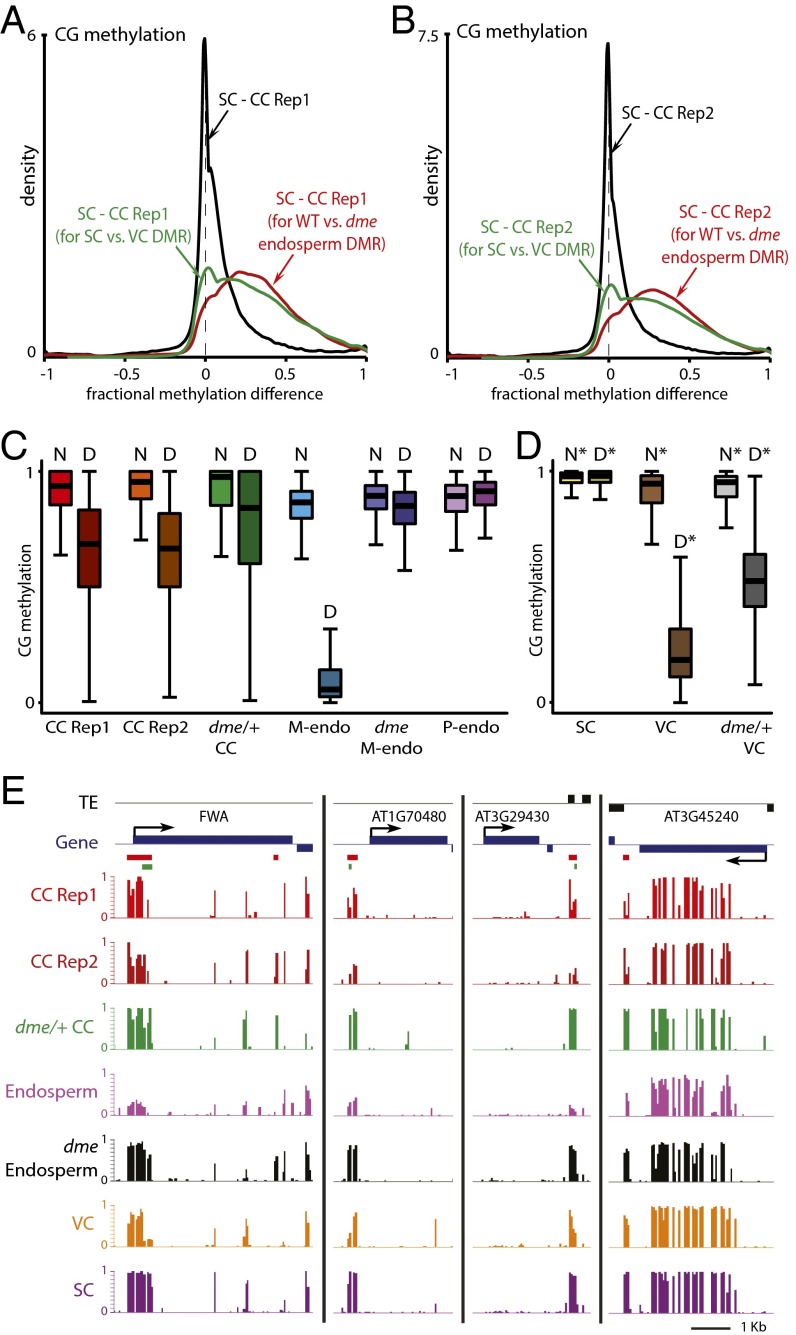
Fig. 3.
DME-dependent demethylation is initiated in Arabidopsis central cells. (A and B) Density plots showing the frequency distribution of CG DNA methylation differences between sperm cell (SC) and central cell (CC) 50-bp windows with at least 10 informative sequenced cytosines in both samples and 70% methylation in one of the samples. The analysis marked by the red trace is confined to differentially methylated regions (DMRs) in the CG context between wild-type and dme mutant endosperm (10). The analysis marked by the green trace is confined to CG DMRs between sperm and vegetative cells (VCs) (10). (C and D) Box plots show CG methylation levels of 50-bp windows in the indicated cell type. Each box encloses the middle 50% of the distribution, with the horizontal line marking the median and vertical lines marking the minimum and maximum values that fall within 1.5 times the height of the box. (C) D, within CG DMRs between wild-type and dme mutant endosperm; M-endo, maternal endosperm; N, outside CG DMRs between wild-type and dme mutant endosperm; P-endo, paternal endosperm. Only windows with methylation greater than 70% in either wild-type or dme mutant endosperm, at least 20 informative sequenced cytosines in both tissues, and at least 20 sequenced cytosines in the graphed sample (10 for central cells) are included. (D) D*, within CG DMRs between sperm and vegetative cells; N*, outside such DMRs. Only windows with methylation greater than 70% in either wild-type sperm or vegetative cell, at least 20 informative sequenced cytosines in both cell types, and at least 20 sequenced cytosines in the graphed sample are included. (E) Snapshots of CG methylation in central cell (CC), endosperm, vegetative cell (VC), and sperm (SC). DMRs between wild-type and dme mutant endosperm are underlined in red; DMRs between sperm and vegetative cells are underlined in green. Previously published data are from ref. 10.