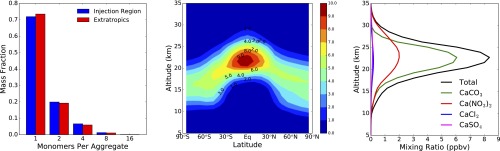
Fig. 1.
Particle aggregation, spatial distribution and chemistry. All plots represent annual average conditions resulting from a 5.6-Tg⋅y−1 steady-state injection of calcite. (Left) The fraction of solid particle mass per sectional bin vs. number of monomers in the fractal aggregate. (Middle) Particle number density (cm−3) as a function of latitude and altitude. (Right) Composition of solid particles resulting from reaction with acids showing total (black line) and CaCO3, CaCl2, Ca(NO3)2, and CaSO4 mixing ratios (parts per billion by volume) averaged from 60°S to 60°N.