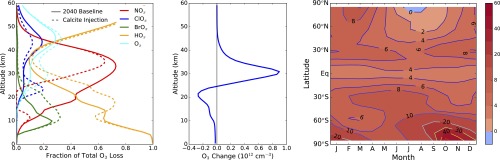
Fig. 2.
Changes in ozone chemistry and distribution. All plots show changes resulting from a 5.6-Tg⋅y−1 steady-state injection of calcite. (Left) Fraction of ozone loss caused by various catalytic cycles as a function of altitude, averaged from 60°S to 60°N for annual average conditions (see Table S1 for definitions of the catalytic cycles). (Middle) Annual average change in ozone (1012 molecules cm−3) as a function of latitude and altitude. (Right) Change in column ozone (percent) as a function of latitude and season.