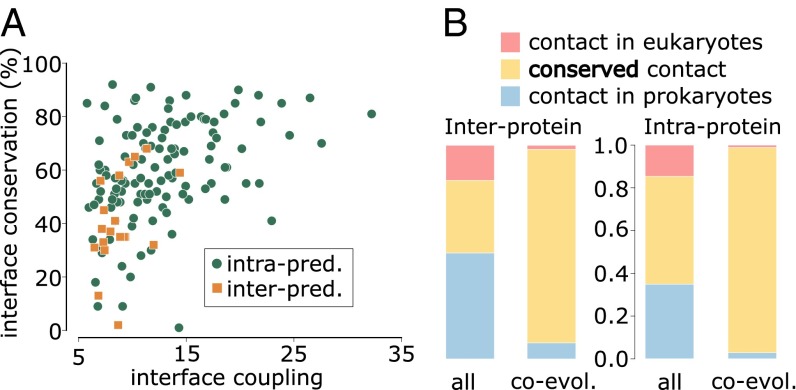
Fig. 2.
(A) Relation between interface structural conservation (defined as in Fig. 1) and interface coupling (the average z-score of the five strongest interdomain coevolving pairs) for 20 interprotein and 121 intraprotein domain–domain interactions with contact predictions (i.e., strong coevolutionary signals) and structurally solved prokaryotic and eukaryotic homologous complexes. (B) Proportion of conserved contacts at the homologous sites of prokaryotic/eukaryotic complexes, computed from the total set of contacts and the subset of coevolving contacts, and for inter- and intraprotein cases. Blue: contacts found in a prokaryotic complex and not in the homologous eukaryotic complex. Red: contacts found in a eukaryotic complex and not present in the homologous prokaryotic complex. Yellow: contacts shared by prokaryotic and eukaryotic complexes. Forty-eight out of 52 coevolving contacts in interprotein complexes and 1,039 out of 1,070 coevolving contacts in intraprotein complexes are shared by prokaryotes and eukaryotes.