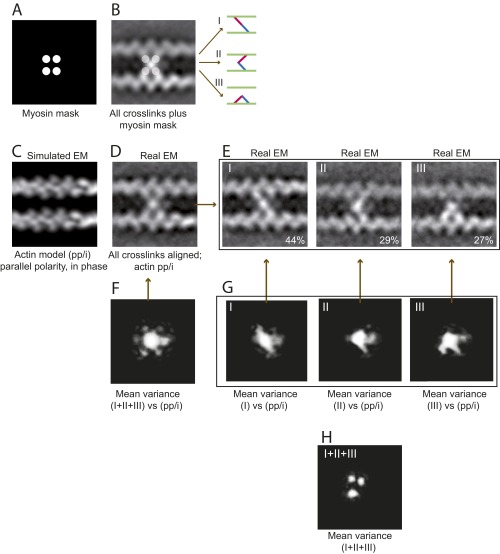
Fig. S3.
EM and image analysis of IXa-MD–induced actin cross-links. All 981 images of actomyosin cross-links were reference free-aligned to generate the first averaged image; actin polarity and phase were not taken into account. (A and B) The EM average indicated that IXa-MD bound to four actin monomers, providing a mask for image classification using HAC and uncovering three distinct binding conformations (I–III). (C) Cross-correlation of the real-EM images with the four actin models (SI Text) showed that 97% of the cross-links were formed between two actin filaments with parallel polarity, aligned in phase (pp/i). (D) Based on this model, 451 EM images with sufficient resolution were realigned and averaged. (E) Classification according to the mask in A was applied once more to the realigned dataset confirming the three distinct conformations. (F) The variance in the global EM average (white intensities) identified the central myosin mass, all four connections to actin, and an extra mass possibly due to the loop 2 calmodulin as parts of myosin-IXa. (G) The variance in the datasets of the three conformations reflected the diagonal, inchworm, and bent myosin conformation and confirmed that IXa-MD attached to only two actin monomers in each conformation. (H) The variance between the class averages confirmed the three distinct actin monomers as the varying second actin-binding site for myosin-IXa.