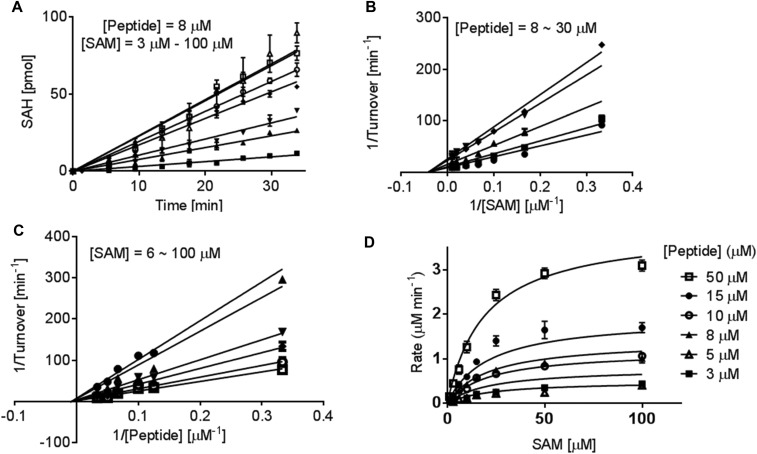
Fig. S1.
Steady-state kinetics and reaction mechanism of SET8-catalyzed H4K20 monomethylation. The kinetic parameters of SET8 methylation were examined using 1 µM SET8 by systematically varying the amount of the H4K20 substrate peptide (3–50 µM) and SAM (3–100 µM). The product of the methylation reaction was quantified with the enzyme-coupled luciferase. (A) Representative initial-rate kinetics for SET8-catalyzed H4K20 methylation with a fixed amount of peptide H4 substrate (8 µM) and varied amounts of SAM cofactor: (■, 3 μM; ▲, 6 μM; ▼, 10 μM; ◆, 15 μM;  , 25 μM;
, 25 μM;  , 50 μM; and ∆, 100 μM). The initial linear range varies with cofactor and substrate concentrations. (B and C) Lineweaver–Burk analysis of the initial velocities vs. varied concentrations of the H4K20 substrate (●, 30 μM; ■, 20 μM; ▲, 15 μM; ▼, 10 μM; and ◆, 8 μM) and SAM (●, 6 μM; ▼,15 μM; ◆, 25 μM;
, 50 μM; and ∆, 100 μM). The initial linear range varies with cofactor and substrate concentrations. (B and C) Lineweaver–Burk analysis of the initial velocities vs. varied concentrations of the H4K20 substrate (●, 30 μM; ■, 20 μM; ▲, 15 μM; ▼, 10 μM; and ◆, 8 μM) and SAM (●, 6 μM; ▼,15 μM; ◆, 25 μM;  , 50 μM; and
, 50 μM; and  , 100 μM). All of the initial rates converge in the secondary quadrant. (D) Global fit of the initial velocities to a general, bisubstrate kinetic mechanism against SAM concentration to afford kcat, Km,SAM, Km,H4K20 and α according to Eqs. S1 and S2 with kcat = 7.0 ± 0.8 min−1, Km,peptide = 40 ± 8 µM, Km,cofactor = 16 ± 6 µM, and α = 1.4 ± 0.8 (45).
, 100 μM). All of the initial rates converge in the secondary quadrant. (D) Global fit of the initial velocities to a general, bisubstrate kinetic mechanism against SAM concentration to afford kcat, Km,SAM, Km,H4K20 and α according to Eqs. S1 and S2 with kcat = 7.0 ± 0.8 min−1, Km,peptide = 40 ± 8 µM, Km,cofactor = 16 ± 6 µM, and α = 1.4 ± 0.8 (45).