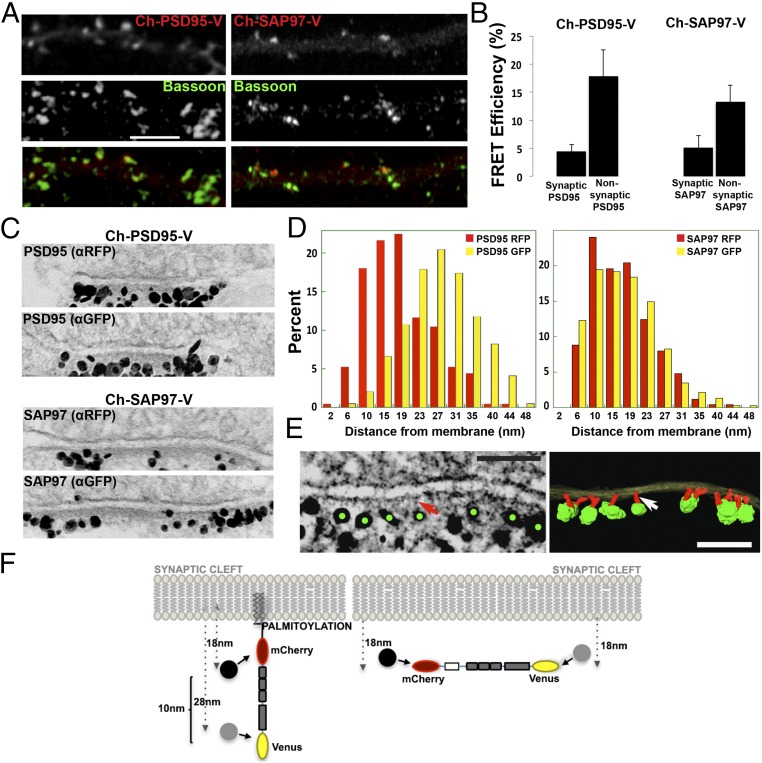
Fig. 3.
Conformation and orientation of PSD95 and SAP97 at synapses. (A) Immunolocalization of Ch-PSD95-V and Ch-SAP97-V at synapses. Ch-PSD95-V (Left) or Ch-SAP97-V (Right) was transfected into cultured hippocampal neurons at 14 days in vitro (DIV). Displayed are dendrites immunolabeled with anti-Bassoon, a presynaptic marker, with Ch-PSD95-V or Ch-SAP97-V expression [FRET construct fluorescence (Top), anti-Bassoon (Middle), merged image (Bottom)]. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (B) FRET efficiency values for Ch-PSD95-V (Left) and Ch-SAP97-V (Right) at synaptic and nonsynaptic regions. At synaptic sites, the FRET efficiency of Ch-PSD95-V was 4.5 ± 1.2%, and at nonsynaptic sites, it was 17.9 ± 4.6% (mean ± SEM; n = 78 puncta, 10 cells, *P < 0.01). At synaptic sites, the FRET efficiency of Ch-SAP97-V was 5.2 ± 2.1%, and at nonsynaptic sites, it was 13.3 ± 2.9% (mean ± SEM; n = 58 puncta, 12 cells, *P < 0.02). (C) Immuno-EM experiment measuring the distance of N and C termini of Ch-PSD95-V (Top) and Ch-SAP97-V (Bottom) from the PSD membrane. Representative EM images of synapses labeled separately with silver-enhanced immunogold particles against RFP (mCherry; Top) or GFP (Venus, Bottom) of Ch-PSD95-V and Ch-SAP97-V at the PSD. (D) Quantification of immuno-EM labeling measuring the distance between anti-RFP–labeled gold particles (red) and the membrane or anti-GFP gold particles (yellow) and membrane. For Ch-PSD95-V, distances were 18 ± 8 nm (mean ± SD; n = 250, 49 spines) for anti-RFP particles and 28 ± 8 nm (n = 784, 37 spines, P < 0.0001 by Student’s t test) for anti-GFP particles. The measured distance between the N-terminal mCherry epitope and the C-terminal Venus epitope was therefore ∼10 nm as summarized in F. For CH-SAP97-V, distances were 17 ± 7 nm (mean ± SD; n = 250, 35 spines) for anti-RFP particles and 18 ± 8 nm (n = 377, 26 spines, P = 0.512) for anti-GFP particles. There was no difference in the measured distance between the N-terminal mCherry and C-terminal Venus epitopes on Ch-SAP97-V. (E) EM tomography on Venus immunolabeled Ch-PSD95-V at PSD. (Left) Tomogram of the immunolabeling of Ch-PSD95-V against the C-terminal Venus site showing silver-enhanced immunogold particles (green dots) at the distal ends of vertical filaments (red arrow). (Scale bar: 100 nm.) (Right) Surface-rendered structural model based on the tomograms. Postsynaptic membrane (translucent yellow), PSD95 molecules as vertical filaments (red; indicated by white arrow), and enhanced immunogold particles (green) are shown. (Scale bar: 100 nm.) (F) Model of PSD95 and SAP97 orientation at the PSD. (Left) For Ch-PSD95-V, the average distance for the N terminus was 18 nm, and it was 28 nm for the C terminus (D), consistent with an orientation perpendicular to the PSD membrane. (Right) In contrast, there was no difference in the distance to the membrane between the N-terminal and C-terminal domains of SAP97 (D), consistent with an orientation parallel to the PSD membrane. The PSD95 extended conformation and orientation perpendicular to the PSD membrane was confirmed by EM tomography in E for Ch-PSD95-V, with anti-GFP sliver-enhanced gold particles in green and PSD95 in red.