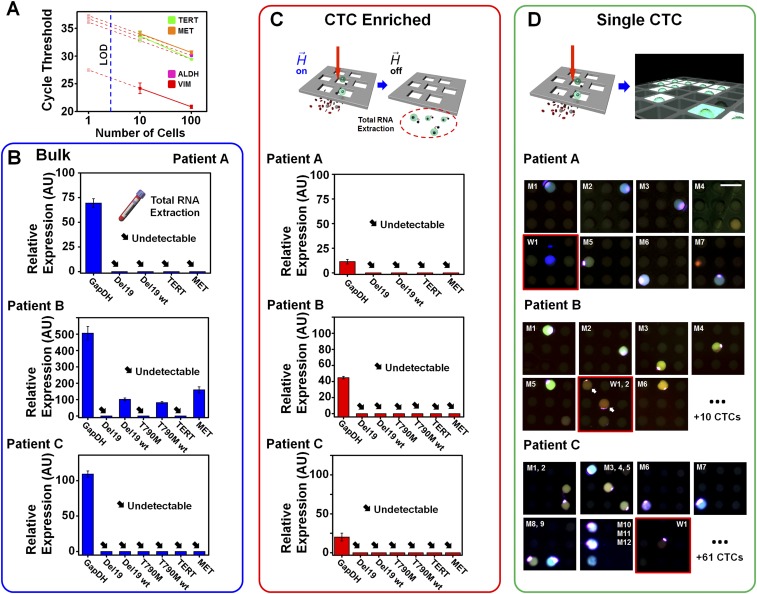
Fig. S5.
Assay performance comparison. (A) Cycle thresholds for PCR on 100 cells, 10 cells, and the theoretical expected value (based on 100 cells) for each of four genes assayed on NSCLC cells. Although the most highly expressed gene, VIM, could be reliably detected for samples of 10 cells, TERT and MET genes displayed deviations from their expected values. Furthermore, the least expressed gene, ALDH, was undetectable for samples of 10 cells. For all four genes, all assays on fewer than 10 cells yielded undetectable signals. These observations highlight the limitations of conventional PCR performed directly on cell eluent populations after enrichment. Assay performance of (B) “Bulk” gene expression directly from whole blood, (C) “CTC Enriched” gene expression after MagSifter processing, and (D) the Nanowell assay for “Single CTC” analysis. From an advanced-stage NSCLC patient with a known EGFR del19 mutation (patient A), assay measurements for putative CTC characterization among Bulk, CTC Enriched, and Single CTC are shown. Bulk and CTC Enriched PCR results indicated that no genes were detected except for constitutive GapDH, thereby showing insufficient sensitivity. The Nanowell assay identified eight CTCs, seven of which exhibited both del19 mutant and its wild-type gene together, with the lone remaining CTC exhibiting the wild type. Assay measurements on an NSCLC patient with a EGFR T790M mutation (patient B) indicated that, although GapDH and other wild-type genes were detected in “Bulk,” no genes were detected. The Nanowell assay identified 18 CTCs, 12 of which exhibited both T790M and its wild-type gene together. The remainders showed the EGFR wild-type gene only. Assay measurements on another NSCLC patient with EGFR del19 mutation (patient C) revealed the same result as patient A. No genes except for constitutive GapDH in Bulk were detected. The Nanowell assay identified 74 CTCs, 42 of which exhibited both del19 mutant and its wild-type gene together. The 32 remaining CTCs exhibited the EGFR wild-type gene only.