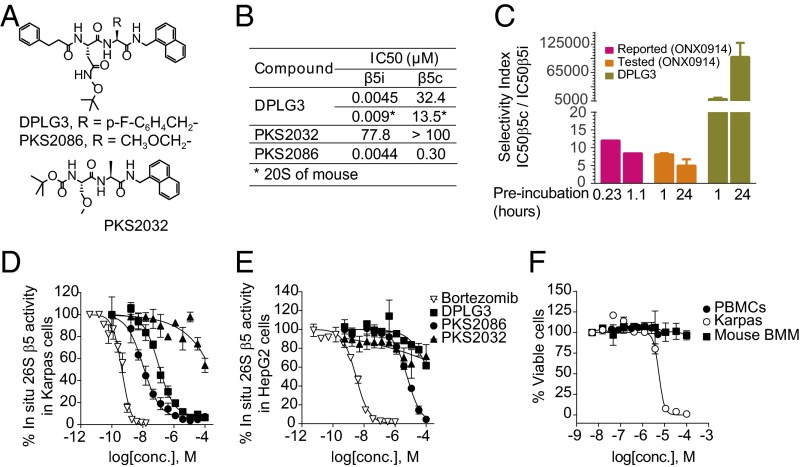
Fig. 1.
Design, rationale, and characterization of noncovalent β5i selective inhibitors. (A) Structures of DPLG3, PKS2086, and inactive congener PKS2032. (B) IC50 values of the compounds against β5i and β5c of human proteasomes and mouse proteasomes, the latter noted by an asterisk (*). Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3). (C) Selectivity indexes of ONX0914 and DPLG3 after 1- and 24-h preincubation with human c-20S and i-20S. “Reported” refers to data from ref. 10. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 2). (D) Inhibition of pan-β5 (β5i and β5c) activities in B lymphoma Karpas 1106P cells (β5i-dominant) and (E) hepatoma HepG2 cells (expressing β5c only) by DPLG3, PKS2086, and inactive congener PKS2032. Bortezomib was used as positive control. Pan-β5 activity was recorded with suc-LLVY-aminoluciferin, measuring luminescence of the hydrolysis product, aminoluciferin. (F) Assessment of DPLG3’s toxicity for PBMCs, mouse bone marrow macrophages (values of EC50 > 100 µM), and Karpas cells (EC50 = 5.53 µM). Data in D–F are means ± SEM (n ≥ 3).