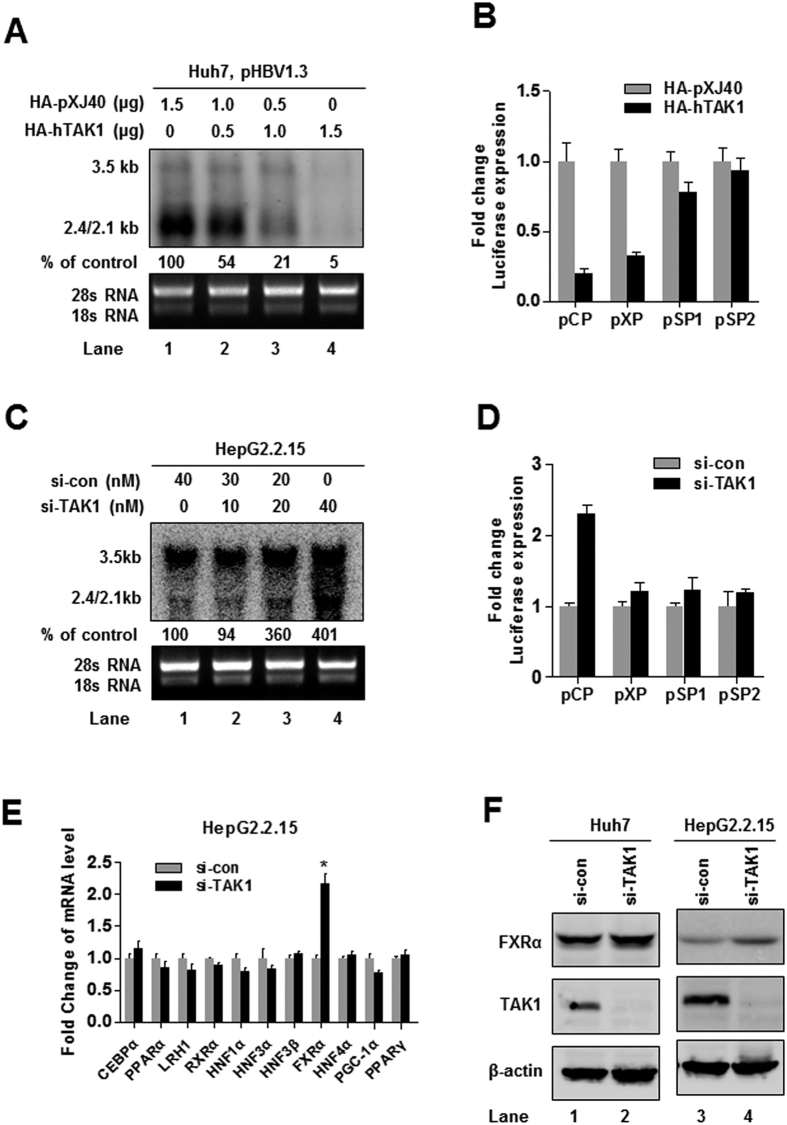
Figure 3. TAK1 regulates HBV core promoter activation through FXRα to suppress HBV transcription.
(A) Huh7 cells were co-transfected with pHBV1.3 and HA-hTAK1 and control vector (HA-pXJ40) as indicated. Levels of HBV RNAs were determined by Northern blot 72 h after transfection. (B) Huh7 cells were co-transfected with 100 ng each of four reporter plasmids containing HBV promoters (pCP, pXP, pSP1, and pSP2) and 100 ng of HA-TAK1 or pXJ40-HA to analyze the effect of TAK1 overexpression on transcription activity from HBV promoters. For each transfection, 100 ng of pRL-TK was included as an internal control for transfection efficiency. Cells were harvested 48 h after transfection, and firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured; luciferase levels were normalized against those generated by the pGL3-basic control plasmid. (C) HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting TAK1 (si-TAK1) or control siRNA (si-con) as indicated. Cells were harvested 72 h after transfection and total cellular RNA were extracted and analyzed by Northern blot. (D) Huh7 cells were co-transfected with 100 ng of each of four reporter plasmids containing HBV promoters (pCP, pXP, pSP1, and pSP2) and 20 nM of si-TAK1 or negative control siRNA. For each transfection, 100 ng of pRL-TK was included as an internal control of transfection efficiency. Cells were harvested 48 h after transfection, and firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured and normalized against those produced by the pGL3-basic control plasmid. (E) HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with si-TAK1 or control siRNA (20 nM). The mRNA levels of associated transcription factors were determined by RT-PCR. (F) HepG2.2.15 cells or Huh7 cells were transfected with si-TAK1 or control siRNA (20 nM) and FXRα and TAK1 expression were verified by western blot.