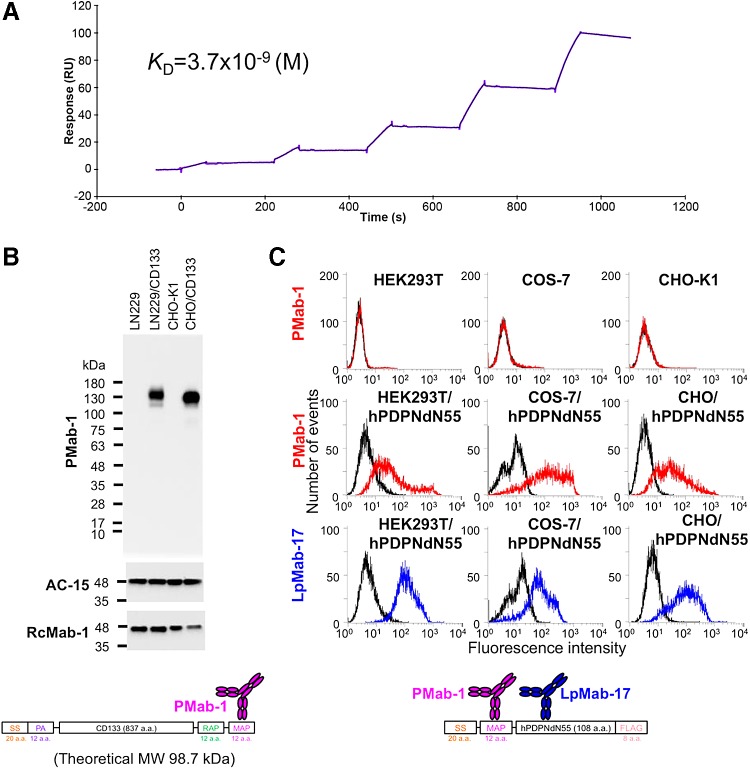
FIG. 1.
Characterization of the MAP tag system. (A) Surface plasmon resonance kinetic analysis of PMab-1 binding toward the MAP tag. Serially diluted, MAP-tagged ATRXepi (12.5, 25, 50, 100, and 200 nM) was injected over the CM5 sensor chip immobilized with PMab-1 for 60 seconds, followed by dissociation in PBST for 120 seconds at a flow rate of 30 μL/min. The binding curve was globally fitted to a 1:1 binding model to derive the equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) values shown. (B) Western blot analysis of MAP tagged CD133 with PMab-1. Total cell lysates (LN229, LN229/CD133, CHO-K1, and CHO/CD133) were electrophoresed under reducing conditions on a 5%–20% SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to a membrane. A membrane containing the same amount of lysate was immunoblotted with 1 μg/mL PMab-1, AC-15, or RcMab-1 for 30 minutes and incubated with peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody specific for rat (PMab-1 and RcMab-1) or mouse (AC-15) IgG. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of MAP-tagged membrane protein. HEK293T, COS-7, and CHO-K1 cells and those transiently transfected with MAP-hPDPNdN55 were incubated with 1 μg/mL PMab-1 or LpMab-17 and stained with Oregon Green 488-labeled secondary antibody specific for rat or mouse IgG. CHO, Chinese hamster ovary; SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; SS, signal sequence.