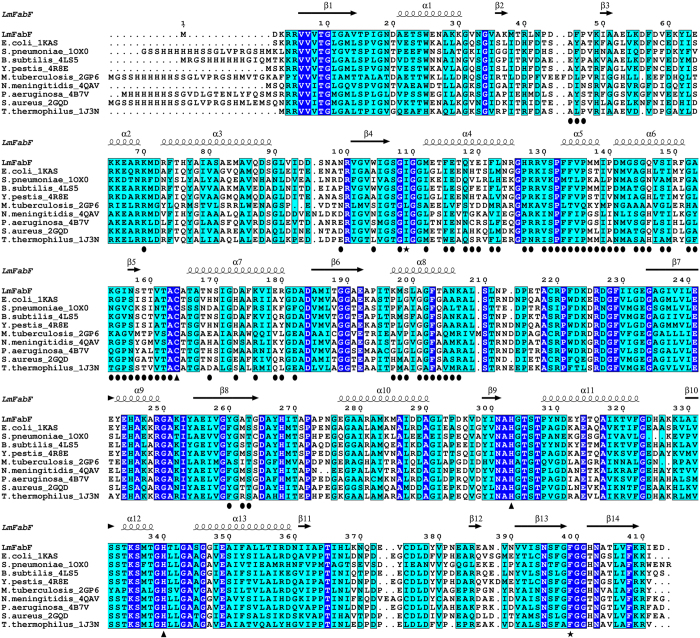
Figure 3. The catalytic triad and surrounding residues of FabF enzymes are highly conserved, as evident in the sequence alignment of LmFabF with FabF from E. coli (PDB: 2GDW), S. pneumoniae (PDB: 1OX0), B. subtilis (PDB: 4LS5), Y. pestis (PDB: 4R8E), M. tuberculosis (PDB: 2GP6), N. meningitidis (PDB: 4QAV), P. aeruginosa (PDB: 4B7V), S. aureus (PDB: 2GQD), and T. thermophilus (PDB: 1J3N).
Strictly conserved residues are highlighted in blue with white text; similar residues are highlighted in cyan; residues of the active site catalytic triad are designated by triangles; residues Ile109 and Phe399, which undergo conformational changes in order to accommodate binding of substrates and inhibitors, are designated by a black star. The α-helices and β-sheets of LmFabF are depicted above their corresponding residues. Interfacing residues of the LmFabF dimer are designated by a black circle.