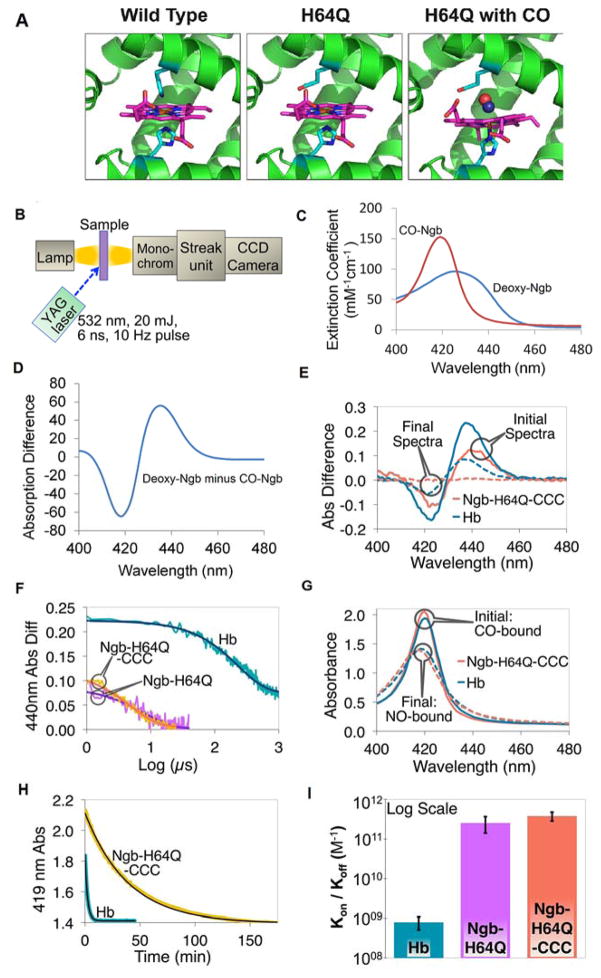
Fig. 1. Kinetics of association and dissociation of CO with hemoglobin and H64Q mutant neuroglobins.
(A) Structure of wild-type Ngb and Ngb-H64Q mutant unliganded and with bound CO. Models for Ngb-H64Q and Ngb-H64Q-CO were built using available Ngb wild-type structures as described in Methods. (B) Flash Photolysis: A laser pulse dissociates CO from the heme. A mercury lamp is used to probe absorption. Light passes through the sample and then is diffracted onto a steak camera so that transmitted light is collected as a function of wavelength and time. For CO recombination kinetics were recorded for 1200 μs, 100 μs, and 50 μs for hemoglobin, Ngb-H64Q, and Ngb-H64Q-CCC, respectively (C) Static absorption spectra of Ngb-H64Q-CCC. Spectra were normalized by concentrations to produce extinction coefficients. (D) Difference spectrum of deoxy-Ngb-H64Q-CCC minus CO-Ngb-H64Q-CCC. (E) Flash Photolysis: Difference between absorbance immediately after photolysis (unliganded protein) and absorbance of CO-protein (“Initial Spectra”) and between absorbance of Ngb-H64Q-CCC 100 μs, or Hb 1200 μs, after photolysis and that of CO-Ngb-H64Q-CCC or CO-Hb (“Final Spectra”). Note: Hb reaction is incomplete after 1000 μs. (F) Flash Photolysis: Kinetics (raw data and fits) of CO binding to the globins on a logarithmic scale, with 1 mM of excess CO (kHb = 4.62 ms−1; kNgb-H64Q = 139 ms−1; kNgb-H64Q-CCC = 188 ms−1) (G) Replacement by NO: Soret band of initial (CO-bound) and final (NO-bound) species for both Hb and Ngb-H64Q-CCC after the addition of 1 mM NO solution. (H) Replacement by NO: Kinetics (raw data and fits) of CO dissociation from Hb and Ngb-H64Q-CCC in presence of 1 mM excess NO (kHb = 7.65×10−3 s−1; kNgb-H64Q-CCC = 4.27×10−4 s−1) (I) The overall affinity was found to be 7.95 ± 2.87 × 108 M−1 for Hb and 2.54 ± 1.13 × 1011 M−1 and 3.80 ± 0.96 × 1011 M−1 for Ngb-H64Q and Ngb-H64Q-CCC, respectively. Error bars show SEM. All the experiments were repeated at least three times.