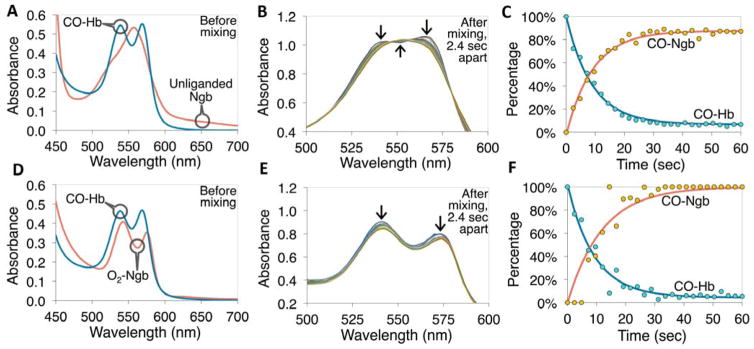
Fig. 2. CO transfer from free hemoglobin to Ngb-H64Q-CCC under anaerobic (A–C) and aerobic (D–F) conditions.
(A) Example absorption spectra of 40 μM CO-Hb and deoxy-Ngb-H64Q-CCC before mixing the two together at 37 °C, in presence of 5 mM sodium dithionite. (B) Spectra measured every 2.4 s after mixing the two proteins together, arrows indicate the change in absorbance at specific wavelengths. (C) Kinetics (deconvoluted data and exponential fits) of the CO-Hb and CO-Ngb-H64Q-CCC species. The measured reaction rate constant was 0.11 s−1 (half-life 6.4 s). (D) Example absorption spectra of 33 μM CO-Hb and 30 μM oxy-Ngb-H64Q-CCC before mixing the two together at 37 °C, in presence of atmospheric oxygen. (E) Spectra measured every 2.4 s after mixing the two proteins together; arrows indicate the change in absorbance at specific wavelengths. (F) Kinetics (deconvoluted data and exponential fits) of the CO-Hb and CO-Ngb-H64Q-CCC species under aerobic conditions. The measured rate constant was 0.11 s−1 (half-life 6.4 s, equal to example in the absence of oxygen). Reference spectra are shown in Fig. S5. All the experiments were repeated at least three times.