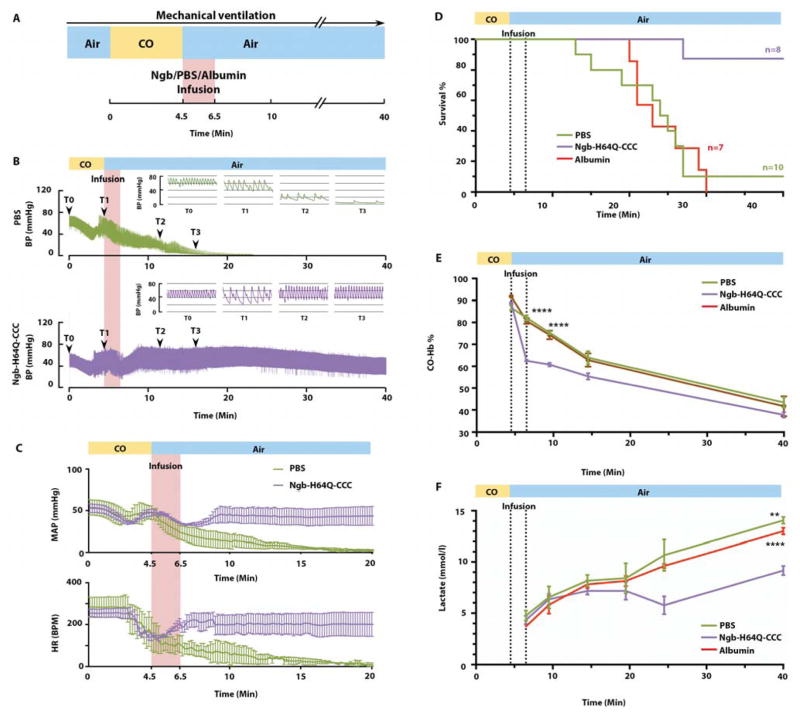
Fig. 5. Ngb-H64Q-CCC increases survival rate in a lethal CO poisoning model.
(A) Experimental scheme of the lethal CO poisoning model. Ventilation was initiated after the surgery with a volume controlled ventilator. 3% CO mixed with air was delivered for 4.5 minutes via the ventilator. Air was delivered after stopping CO exposure and the Ngb-H64Q-CCC or PBS/albumin control was infused within 2 minutes. All mice were followed for a pre-defined experimental observation period of 40-minutes. (B) Mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) changes in mice treated with PBS and Ngb-H64Q-CCC. All data are expressed as means ± SEM. (C) Representative MAP changes in one mouse treated with PBS and one Ngb-H64Q-CCC treated survivor. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of mice exposed to 3% CO for 4.5min treated with PBS only (n = 10), albumin 5mM (n = 7) or Ngb-H64Q-CCC (n = 8) (Log-rank test survival, P = 0.0008). (E) Time course of RBC-encapsulated CO-Hb with Ngb-H64Q-CCC (n = 3) vs. PBS (n = 4) and albumin (n=4) in lethal CO poisoning model. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, P < 0.0001. (F) Lactate level elevation is lessened with Ngb-H64Q-CCC treatment (n = 3) vs. PBS (n = 4) and albumin (n = 4) in lethal CO poisoning.