Figure 3.
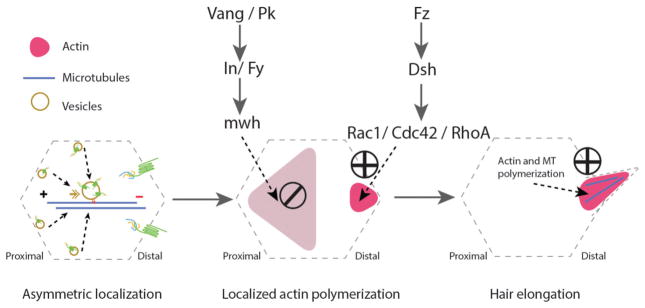
Cytoskeletal arrangements during the planar cell polarization process in Drosophila pupal wing epithelial cells. uring pupal development, epithelial cells use essential cellular machinery, including the protein trafficking machinery which is involved in the asymmetric localization of the Fz-PCP core components in a polarized manner. This directed transport requires an alignment of well oriented microtubules (MT, blue line in left panel) with enriched minus-ends towards the distal side of each cell (left panel). This stage is followed by activation of actin polymerization in the distal side (via Fz-Dsh signaling), while blocking actin polymerization in the proximal side (via Vang-Pk and their effectors) of the same cell (middle panel). The last stage involves actin and stable microtubule polymerization at the base and inside trichomes (cellular hairs), which is essential for hair elongation (right panel).