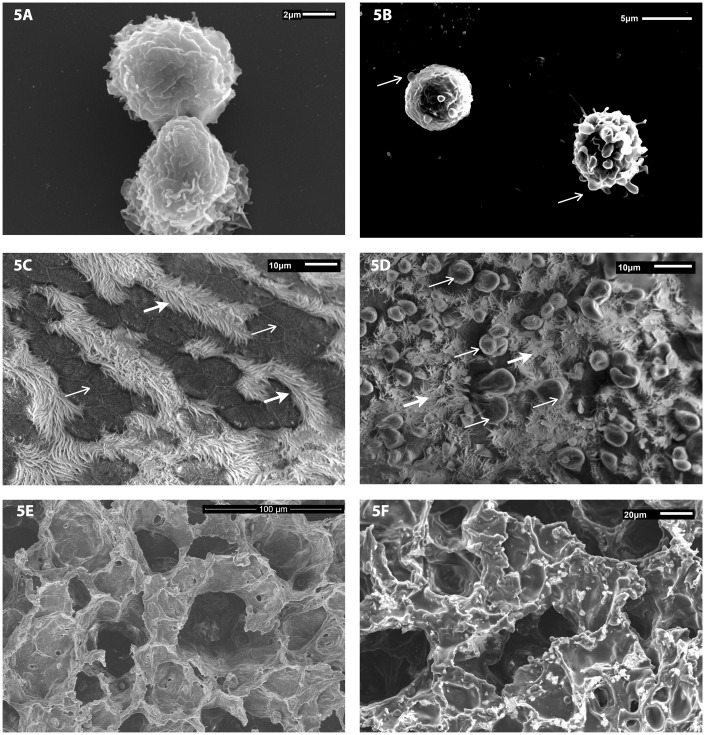
Figure 5.
Representative scanning electron micrographs of pulmonary macrophages isolated from BALF of animals exposed by inhalation to a concentration of 10 mg/m3 of WO3 NPs. Cellular fractions of BALF were seeded on coverslips with RPMI 1640 media. SEM photomicrographs of lung tissue from control and treated animals were fixed in 3% glutaraldehyde and processed as described in methods. (a) Macrophages from control animals had a ruffled surface, typical of phagocytes while those from WO3 NPs exposed animals’ (b) had surface membrane blebs (arrow) that are a characteristic feature of apoptosis. (c) The surface of airways from control animals had no sign of membrane damage, with rows of cilia (open arrow) and intercellular tight junctions clearly visible (arrow). (d) In contrast, the luminal surface of airway epithelia of hamsters treated with 10 mg/m3 of WO3 NPs displayed numerous membrane blebs (arrows) with interspersed cilia (open arrow). (e) SEM images of alveolar surfaces from controls lacked WO3 NPs and had an unremarkable appearance. (f) Photomicrographs of alveolar surfaces show a granular deposition of WO3 NPs