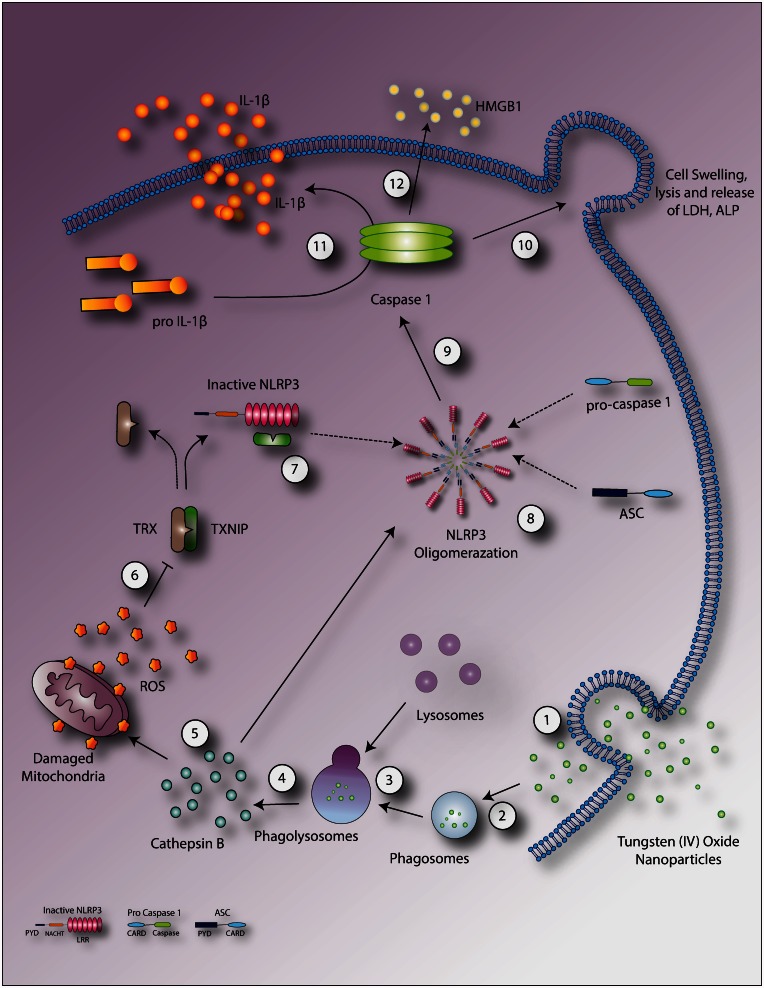
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of proposed mechanisms mediated by WO3 NPs. WO3 NPs enter into cell (1) through the membrane or in the form of a phagosome (2), resulting in lysosomal fusion (3) with phagolysosome causing disruption and cytoplasmic release of cathepsin B (4). Alternatively, the free particles in cytoplasm may directly interact with cellular components such as mitochondria leading to oxidative stress. Cathepsin B mediates direct NLRP3 oligomerization or ROS formation via mitochondrial membrane disruption (5). ROS in turn facilitates the dissociation of TXNIP from its inhibitor TRX (6). Newly dissociated TXNIP, binds to inactive NLRP3 (7) resulting in NLRP3 activation and subsequent oligomerization (8) which activates caspase-1 (9). Active caspase-1 mediates cell swelling and lysis (10), the cleavage of pro-IL-1β to IL-1β (11) and the release of HMGB1 (12). (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)