FIGURE 2.
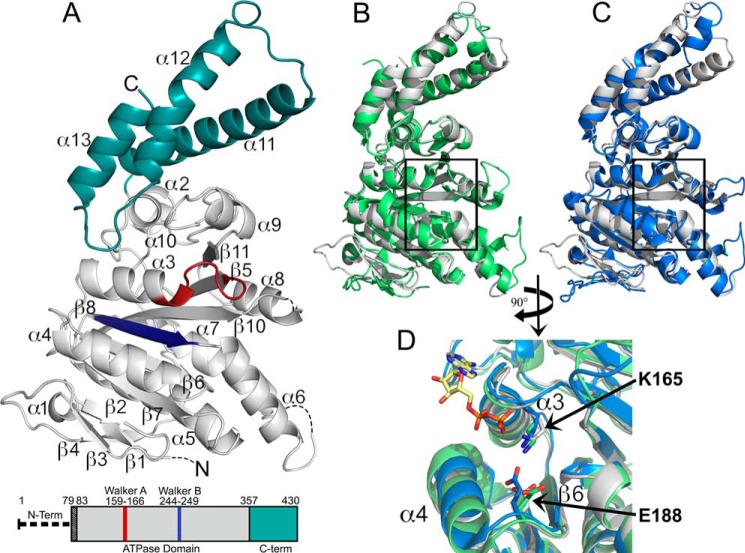
2.4 Å X-ray crystal structure of the Shigella T3SS ATPase Spa47. A, crystal structure of Spa47Δ1–79 with coloration corresponding to the predicted domains highlighted in the bar diagram of the Spa47 sequence, where the truncated N-terminal oligomerization domain is represented by a thick dashed line and the black-shaded region corresponds to the N-terminal residues of the construct that are not included in the structure. The gray portion of the Spa47 structure corresponds to the catalytic ATPase domain, the cyan region represents the C-terminal domain, and the Walker A (P-loop) and B motifs are shown in red and blue, respectively. The secondary structure elements are identified, and the dashed lines within the Spa47 structure represent disordered regions with unassigned structure (four N-terminal residues and those connecting α6-β7 and α8-β10). β9 is located directly behind β10 and not visible in this orientation. B and C, alignment of Spa47 (gray) with the catalytic ATPase and C-terminal domains of FliI (green, B) and EscN (blue, C) illustrates the high degree of conservation within the catalytic core of the related ATPases, especially within the nucleotide-binding region (black boxes). D, a closer view of the nucleotide binding site within the aligned structures identifies the conserved active site Lys165 and Glu188 residues positioned near the FliI-bound ADP shown with a yellow carbon skeleton. The PDB codes for the Spa47, FliI, and EscN structures are 5SWJ, 2DPY, and 2OBM, respectively. The crystal structures were rendered using PyMOL.