FIGURE 9.
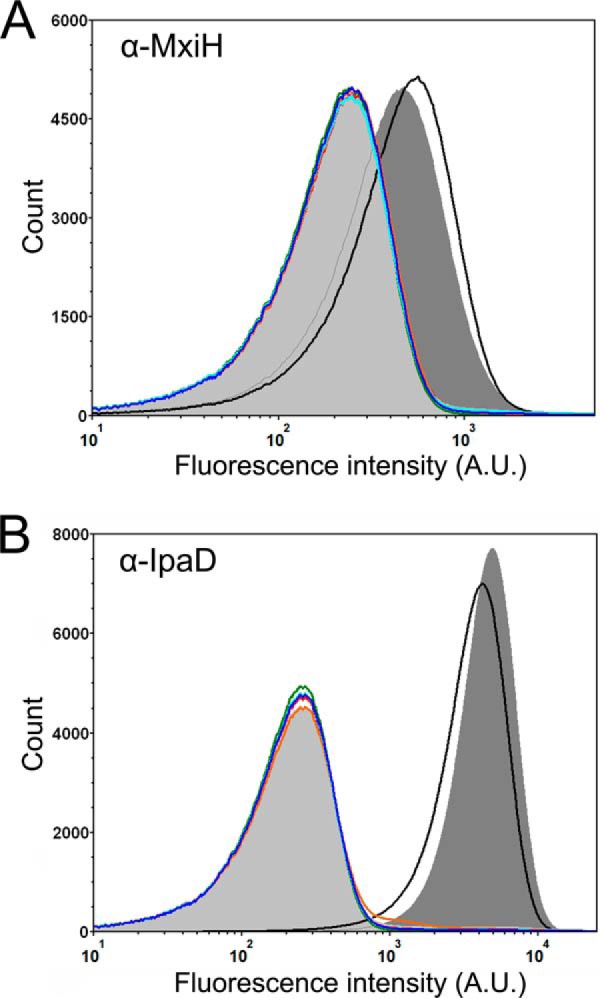
Flow cytometry detection of surface localized Shigella T3SS components. A, fluorescence intensity histograms depicting the levels of surface localization of MxiH for the S. flexneri 2457T strain (black), mxiH null strain (orange), spa47 null S. flexneri strain (light gray shading), and the spa47 null strain complemented with wild-type Spa47 (dark gray shading), Spa47K165A (red), Spa47E188A (blue), Spa47R350A (cyan), and Spa47Δ1–79 (green). B, fluorescence intensity histograms depicting the levels of surface localization of the T3SS tip protein IpaD for the same strains shown in A. The histograms include 500,000 individual intensity measurements per condition and are representative of independent triplicate analysis. The decreased levels of the MxiH and IpaD for all of the ATPase inactive Spa47 mutants are consistent with the in vitro experiments, suggesting that Spa47-catalyzed ATP hydrolysis drives/supports T3SA needle formation and Shigella virulence.
