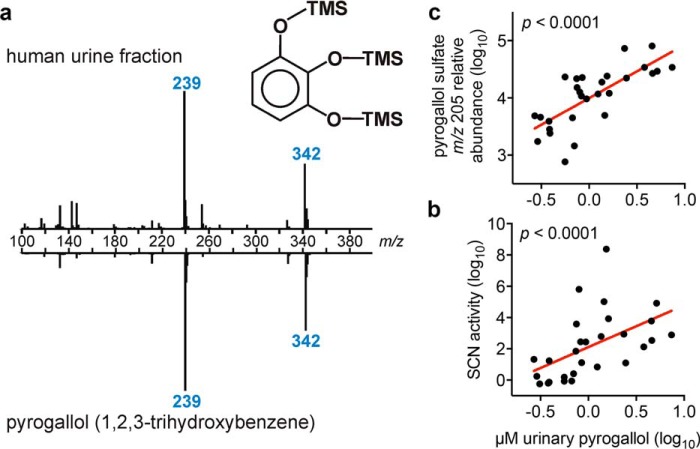
FIGURE 6.
Urinary pyrogallol is significantly correlated with SCN antimicrobial activity. Urinary pyrogallol concentration, as confirmed by GC-MS (a), was found to increase significantly (p < 0.0001, Pearson correlation) with increasing SCN antimicrobial activity as defined in a previous study (14) (b). Furthermore, elevated molar concentrations of pyrogallol were also significantly correlated (p < 0.0001, Pearson correlation) with sulfated pyrogallol relative abundance as detected by LC-MS/MS (c). Each point represents data from a single donor urine specimen. Linear regression of log-transformed values (red lines) yielded r = 0.52 and slope = 2.68 ± 0.87 (b) and r = 0.74 and slope = 0.93 ± 0.17 (c).