FIGURE 9.
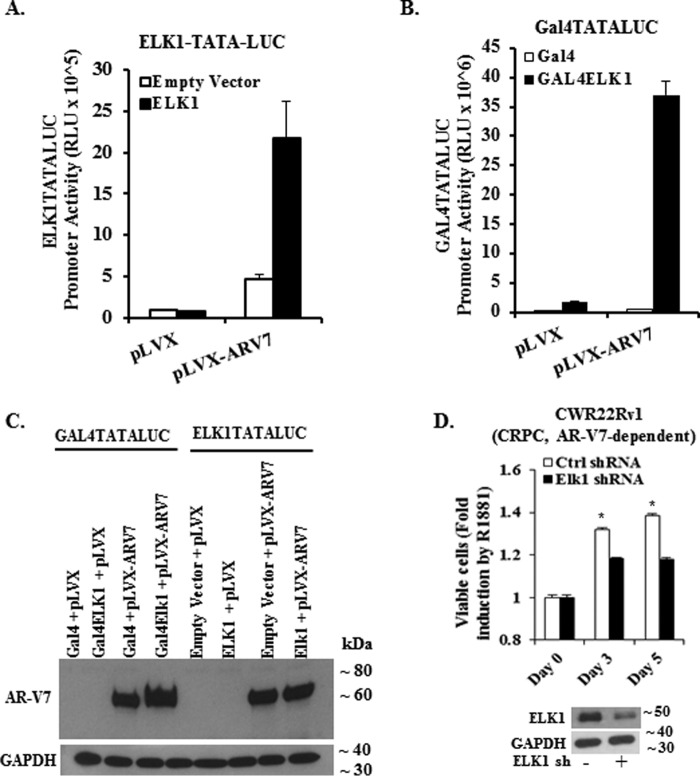
Functional association of ELK1 and AR-V7 and effect on cell growth. A, HeLa cells were co-transfected with an ELK1-driven minimal promoter-luciferase reporter ((ELK1)2-TATA-LUC) and expression plasmid for either AR-V7 or WTELK1 or control vector plasmid for 48 h. Luciferase activity was measured in the cell lysates. For all transfections, a Renilla luciferase reporter was used as the control for transfection efficiency. B, HeLa cells were co-transfected with a Gal4-driven minimal promoter-luciferase reporter (Gal4-TATA-Luc) and expression plasmid for either AR-V7 or Gal4-ELK1 or control vector plasmid for 48 h. Luciferase activity was measured in the cell lysates. For all transfections, a Renilla luciferase reporter was used as the control for transfection efficiency. C shows a Western blot of HeLa cell lysates corresponding to all of the transfections in A and B, which was probed using an antibody to the amino-terminal domain of AR or with antibody to GAPDH (loading control). D, top panel shows the effect of depleting ELK1 by lentiviral shRNA transduction on the growth of CWR22Rv1 cells monitored by the MTT assay compared with control shRNA. The Western blot in the bottom panel shows ELK1 shRNA-induced depletion of ELK1 compared with control shRNA; GAPDH was probed as the loading control.