FIGURE 4.
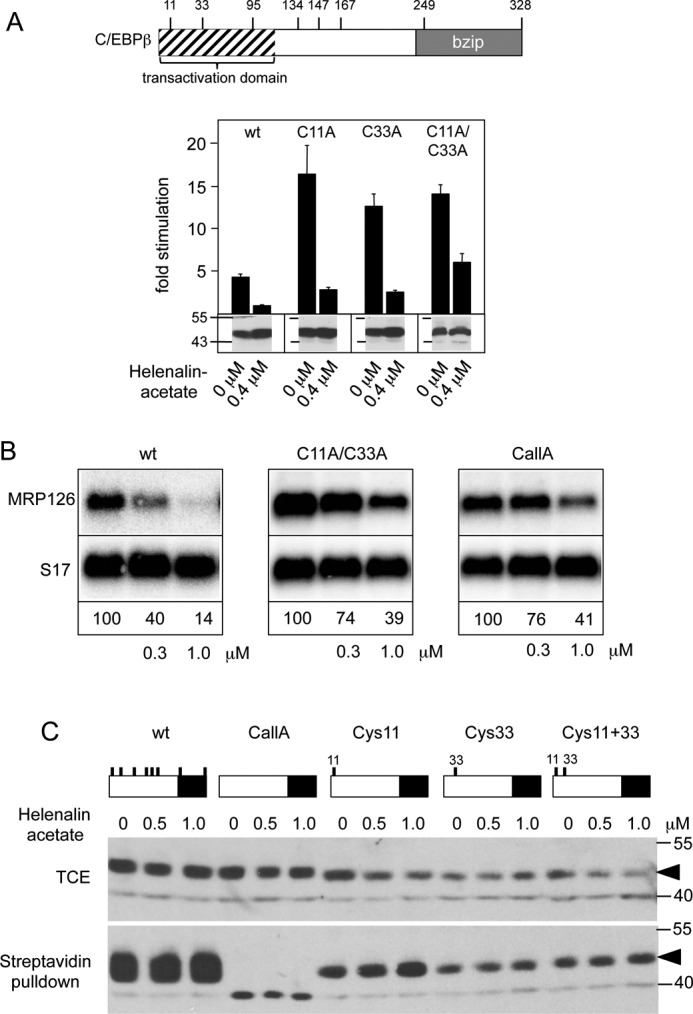
Inhibition of C/EBPβ activity by helenalin acetate is not due to the alkylation of cysteine residues of C/EBPβ. A, the positions of cysteine residues of C/EBPβ are shown schematically at the top. The panel below illustrates reporter assays with C/EBPβ mutants lacking Cys-11 or Cys-33 or both. Reporter assays were performed as in Fig. 1A. Aliquots of the cell extracts were used to visualize the amounts of C/EBPβ (bottom panels). Error bars show the S.D. B, QT6 cells were transfected with expression vectors for wild-type or C/EBPβ mutants lacking cysteines 11 and 33 (C11A/C33A) or all cysteines (CallA) and treated with the indicated concentrations of helenalin acetate. Cells were harvested after 12 h and analyzed by Northern blotting for expression of MRP126 and S17 mRNAs. The numbers below the blots indicate the relative expression levels of MRP126 mRNA. C, QT6 cells were transfected with expression vectors for the different C/EBPβ mutants (containing only the indicated cysteine residues) and treated for 12 h with or without helenalin acetate, as indicated. Cell extracts were then subjected to biotinylation with BMCC-Biotin, followed by incubation with streptavidin agarose. Total cell extracts (TCE) and bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting, using antibodies against C/EBPβ. Numbers on the side of the Western blots in A and C refer to molecular weight markers.
