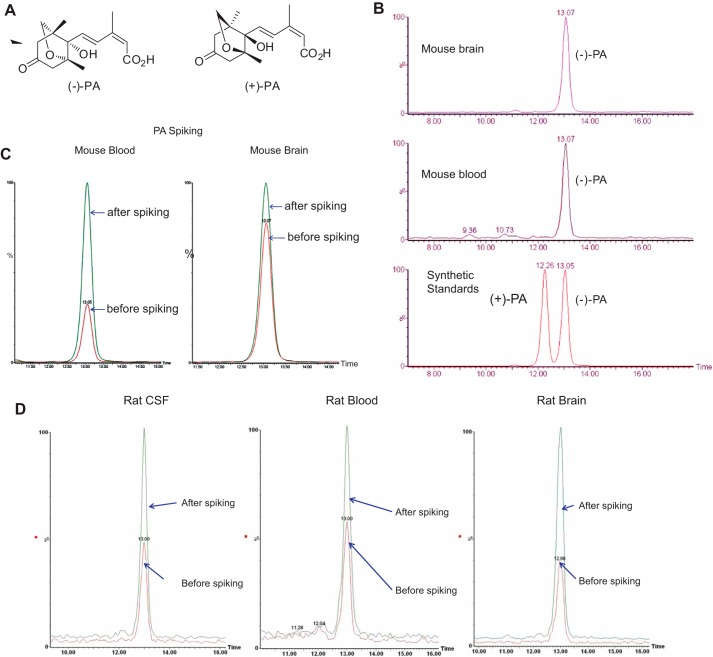
FIGURE 1.
Identification and characterization of PA in rodent brains. Chemical structures of (+)-PA and (−)-PA are shown in A. Near baseline enantioseparation of PA in standard solutions was achieved by a gradient elution mode as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Brain and blood samples were subjected to UPLC/MS/MS using a chiral column and then compared with known standards shown in B. Spiking experiments of brain and blood samples with known amounts of standards were also performed to confirm that only naturally occurring (−)-PA was present in mouse (B and C) and rat (D) tissues.