FIGURE 6.
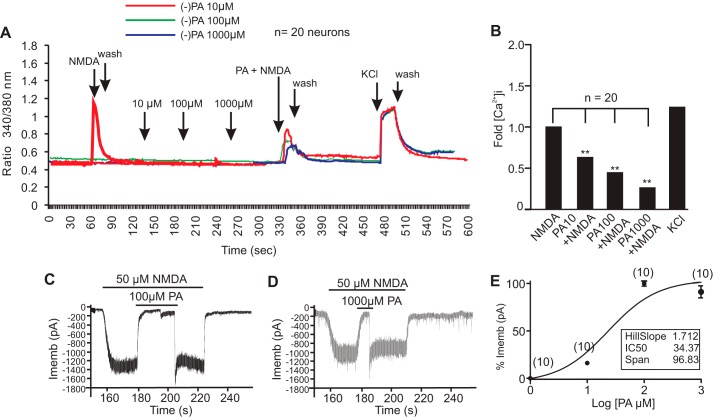
Reversible inhibition of NMDA receptors by (−)-PA. A, ratiometric calcium imaging. Cultured cortical neurons on glass coverslips were loaded with Fura-2 AM for 30 min followed by washing with PSS or HBSS buffer. (−)-PA at the indicated concentrations was added to neurons. Fura-2 fluorescence from more than 10 selected neurons was measured for up to 30 min. After washing with PSS or HBSS buffer, NMDA with or without (−)-PA at the indicated dosage was loaded onto neurons. Addition of KCl showed a large [Ca2+]i, confirming that these neurons were functional cells. Changes in calcium were measured by converting the 340/380 ratio of Fura-2 florescence (after correction for background) as described. Data obtained from at least three independent experiments (n = 20 cells) were averaged and plotted (B). Representative NMDA currents activated by 50 μm NMDA plus 1 mm glycine and their inhibition by 100 and 1000 μm (−)-PA are shown in C and D, respectively. (−)-PA was first applied for 30 s and then simultaneously applied with NMDA. Membrane potential was clamped at 270 mV. E shows the (−)-PA concentration-response relationship for inhibition of NMDA currents activated by 50 μm NMDA plus 1 μm glycine. The concentration-response curve was fitted by the logistic equation with an IC50 value of 34.37 ± 0.012 μm and a Hill slope factor of 1.712 ± 0.038 (n = 10). Data in E represent the average of 10 neurons. Error bars represent the mean ± S.E. ** indicates p < 0.05 compared with NMDA group in B using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc analysis (n = 20). Imemb, total transmembrane ionic current.