FIGURE 7.
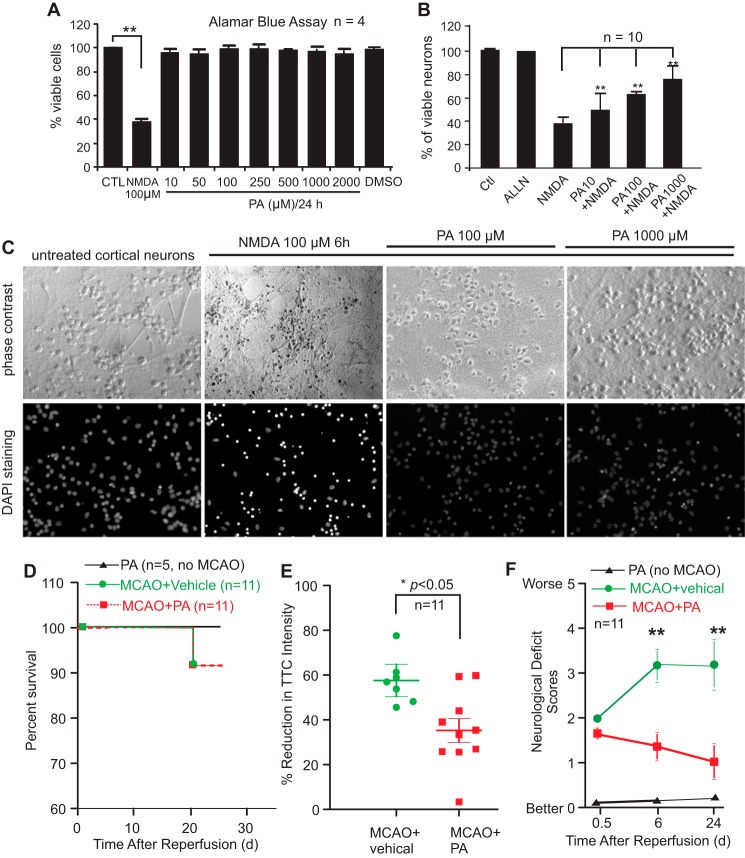
(−)-PA protects cultured cortical neurons against glutamate toxicity and reduces ischemic brain injury. Neuronal viability was assessed using the Alamar Blue assay. NMDA at 100 μm reduced cellular viability to 40% compared with the untreated control (A). (−)-PA alone has no toxicity to neurons (A). Adding (−)-PA to NMDA-treated neurons significantly protected cells from death (B). DAPI staining of cellular nuclei is shown in C. Data represent the mean ± S.E. ** indicates p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc analysis; n = 5). D–F, (−)-PA protects mouse brain from MCAO-induced damage. Mice were subjected to 1 h of MCAO and 24 days of reperfusion as described under “Experimental Procedures.” An osmotic pump was preimplanted before MCAO surgery to deliver (−)-PA into the ischemic side of the brain ventricle as described under “Experimental Procedures.” (−)-PA was also delivered to non-MCAO mice, which served as a control. D, mouse survival rate was plotted. (−)-PA itself or administered into MCAO mice did not alter significantly the survival rate as this MCAO model has a very low mortality rate to begin with. Brain slices were stained with TTC, and soluble TTC was extracted and measured using a spectrophotometer (E). Quantification of TTC staining showed a significant reduction in brain infarction compared with the vehicle-treated mice (E; *, p < 0.05, paired t test; n = 11). Neurological deficit scores were also measured at 0.5 h, 6 days, and 24 days after MCAO and reperfusion (F). Error bars represents the mean ± S.D. ** indicates p < 0.01 by paired t test. CTL, control.