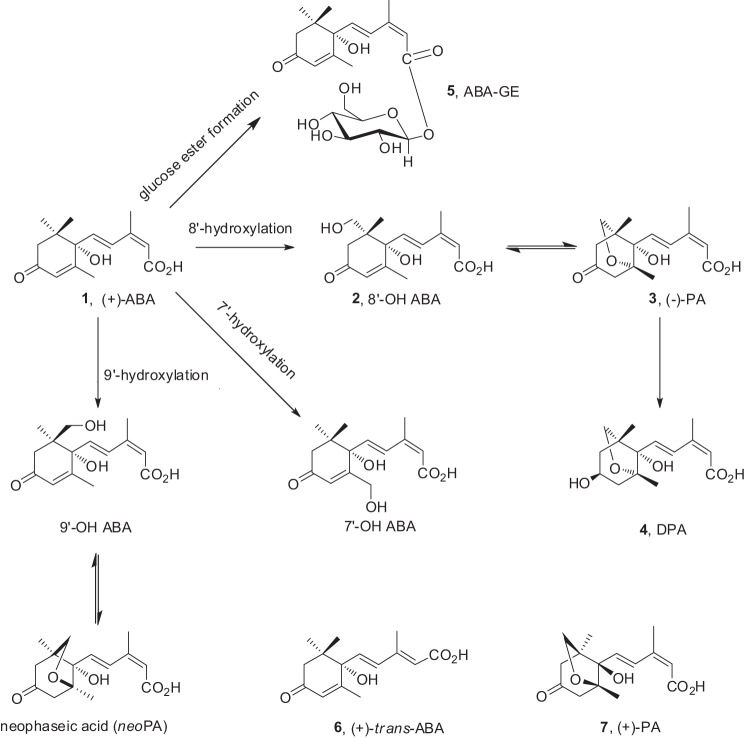
FIGURE 9.
Known metabolic pathways of (+)-ABA in plants. The principal oxidative pathway of natural (+)-ABA (1), mediated by cytochrome P-450 monooxygenases, occurs through hydroxylation of the 8′-methyl group resulting in 8′-hydroxy-ABA (2), which rearranges to PA (3). Further enzymatic reduction of PA leads to DPA (4). Other metabolic steps include hydroxylation of the 7′- and 9′-methyl groups of the ABA ring as well as the conjugation of glucose esters (ABA-GE; 5). In plants, trans-ABA (6) is a product of isomerization of natural ABA under UV light. The unnatural mirror image form of PA (7) may also occur as a result from the feeding of unnatural (−)-ABA.