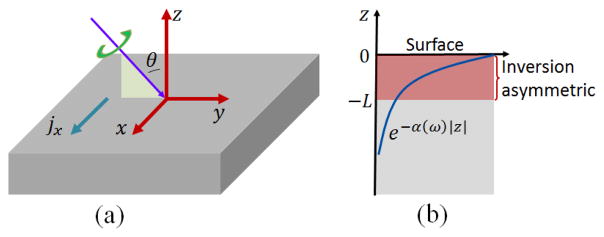
FIG. 1.
(a) Schematic of the circular photogalvanic measurement. The incident light with right circular polarization is propagating within the ŷ-ẑ plane (indicated by the light green triangle) with incidence angle θ. Inversion symmetry breaking is assumed along ẑ direction. Photocurrent is flowing perpendicular to the plane of incidence. In our model system, the photocurrent is along the x̂ direction. (b) Schematic of a situation that the inversion asymmetry is only present over a distance L from the sample surface indicated by the pink rectangle. The light intensity follows an exponential decay e−α(ω)|z| with α(ω) being the absorption coefficient and |z| being the distance away from the surface.