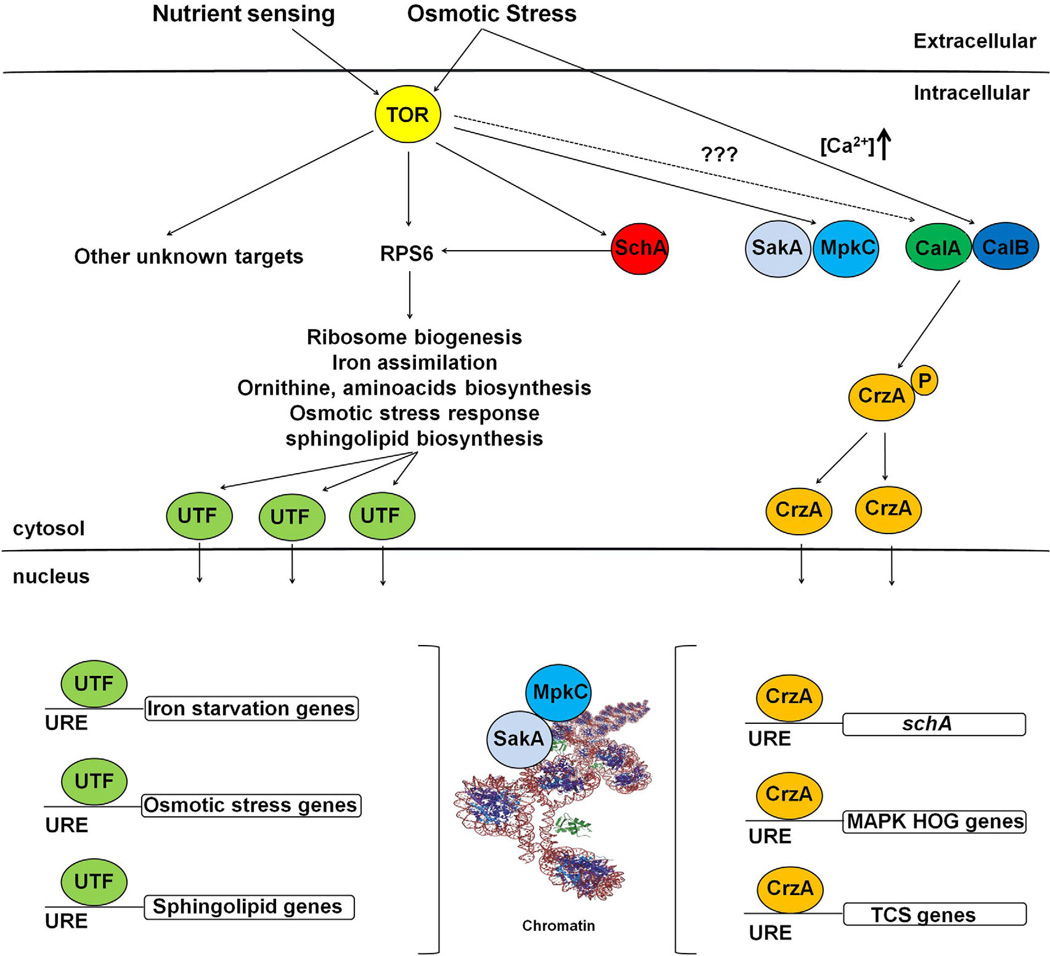
Fig. 12.
A possible model for the interaction between A. fumigatus SchA, calcineurin/CrzA and SakA/MpkC during nutrient sensing and osmotic stress. A. fumigatus TOR phosphorylates SchA and Rps6 SchA during nutrient sensing or osmotic stress. SchA also phosphorylates Rps6 and other targets, and activates unknown transcription factors (UTF). UTFs will be transported to the nucleus via importins and bind to upstream regulatory elements (URE), activating targets related to ribosome biogenesis, iron assimilation, ornithine, amino acids biosynthesis, osmotic stress response and sphingolipids biosynthesis. Upon osmotic stress, there is an increased (Ca +2) released in the cytoplasm, activating the calcineurin complex (CalA and CalB are the catalytic and regulatory subunits respectively) that will dephosphorylate the transcription factor CrzA. CrzA will be transported to the nucleus via importins and bind to UREs, activating genes encoding MAP kinases of the HOG/SakA pathway and proteins of the two-component system (TCS). Upon increased (Ca +2), CrzA binds to the schA URE activating transcriptionally this gene. It is not known if there is any interaction between TOR and calcineurin/CrzA. The MAPK SakA and MpkC are controlled by TOR and will be translocated to the nucleus upon nutrient sensing or osmotic stress and will interact with the chromatin. It is likely MpkC modulates SakA and both phosphorylate several of the UTFs to activate them as transcription factors.