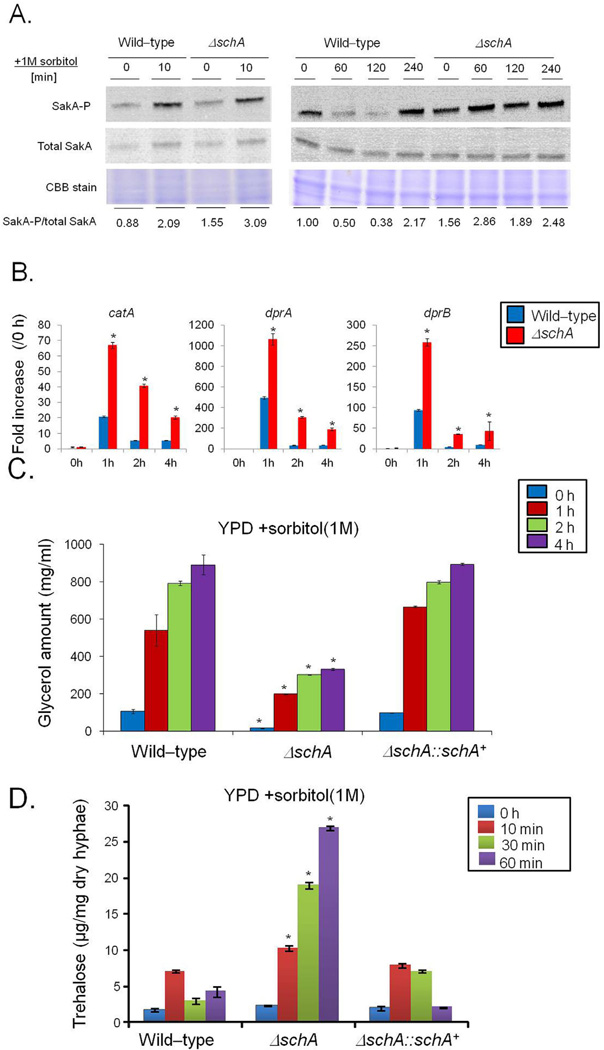
Fig. 3.
The schA null mutant has increased SakA phosphorylation.
A. Immunoblot analysis for SakA phosphorylation in response to osmotic stress. The wild-type and the schA null mutant were grown for 18 h at 37°C. Then, sorbitol (1 M final concentration) was not added (control) and added for 0 (control), 10, 60, 120 and 240 min. The mycelium was harvested at the indicated times, and total proteins were extracted. Anti-phospho-p38 was used to detect the phosphorylation of SakA, and anti-Hog1p was used to detect the total SakA protein. A Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB)-stained gel is shown as a loading control. Signal intensities were quantified using the Image J software by dividing the intensity of SakA-P/SakA ratio and expressed as fold increase from the control (0 min).
B. The ΔschA mutant shows higher expression of osmostress dependent genes. The wild-type and the ΔschA mutant were grown for 18 h at 37°C. Then, sorbitol (1 M final concentration) was added for 0 (control), 1, 2 and 4 h. The mycelium was harvested at the indicated times, and total RNA was extracted. The absolute quantitation of catA, dprA, and dprB and actA (Afu6g04740, encoding the actin) was determined by a standard curve (i.e., CT -values plotted against a logarithm of the DNA copy number). The results are the means (± standard deviation) of four biological replicates (*, p < 0.001, comparison of the treatments with wild-type).
C and D. Glycerol and trehalose accumulation in the wild-type, ΔschA, and ΔschA::schA+ strains upon osmotic stress. The strains were grown for 18 h at 37°C. Then, sorbitol (1 M final concentration) was added for 0 (control), 1, 2 and 4 h. Glycerol and trehalose were quantified and normalized according to the volume of the lysate or dry weight respectively. The results are the means (± standard deviation) of three biological replicates (*, p < 0.001, comparison of the treatments with wild-type).