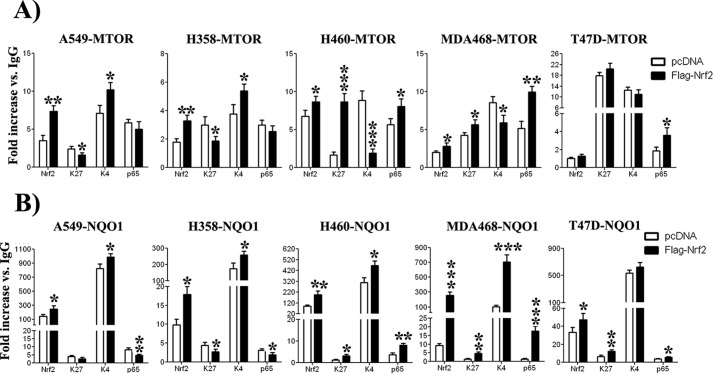
FIGURE 7.
PI3K pathway activation status differentially affected changes in histone modifications as well as p65 binding to MTOR promoter. A, Nrf2 overexpression led to its increased binding to MTOR promoter. This led to different results depending on the activation state of PI3K pathway. In A549 and H358, which have physiologic PI3K pathway, increased Nrf2 binding led to increased H3-K4me3 signal parallel to a small decrease in H3-K27me3 and in p65 binding. In H460 and MDA468, both hosting abnormally activated PI3K pathway, increased Nrf2 binding resulted in higher p65 binding and higher H3-K27me3 signal, concomitant with a decrease in H3-K4me3 levels. In T47D cells, Nrf2 induction did not result in significant increase in Nrf2 binding, and no significant change was observed in H3-K27me3 and H3-K4me3 signals as well as p65 binding. B, Nrf2 overexpression led to its increased binding to NQO1 promoter. This led to decreased H3-K27me3 signal and p65 binding, whereas no significant change was observed in H3-K4me3 mark in A549 and H358 cells. In H460, MDA468, and T47D, H3-K27me3 mark and p65 binding were increased, whereas H3-K4me3 was significantly increased in H460 and MDA468 cells. -Fold increase data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with pcDNA-transfected controls.