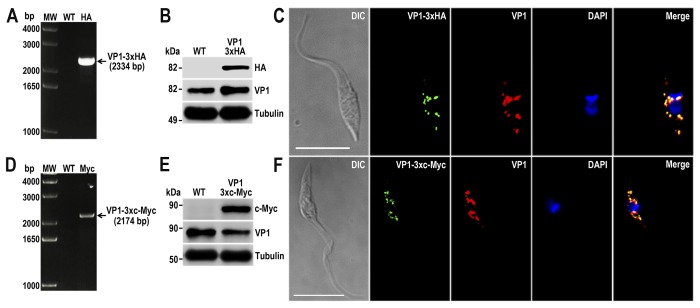
FIGURE 2.
TcVP1 endogenous C-terminal tagging. A, PCR analysis using gDNA isolated from WT and TcVP1–3×HA cell lines. A DNA fragment was amplified in 3×HA-tagged epimastigotes (indicated with arrow), whereas the band is absent in WT. B, Western blotting analysis of WT and TcVP1–3×HA cell lines. Anti-HA antibodies detect TcVP1–3×HA (expected size, 89 kDa), and anti-TbVP1 antibodies detect endogenous TcVP1 (85 kDa). Anti-α-tubulin antibody was used as a loading control. Antibodies are indicated on the right side of the blots, and molecular weights (MW) are on the left side. C, fluorescence microscopy of TcVP1–3×HA epimastigotes indicates localization of the endogenous tagged protein to acidocalcisomes. TcVP1–3×HA was detected with monoclonal anti-HA antibodies (green) or with polyclonal anti-TbVtc4 antibodies (red). D, PCR analysis of TcVP1–3×c-Myc epimastigotes. A DNA fragment was amplified in c-Myc-tagged epimastigotes (indicated with arrow), whereas the band is absent in WT cells. E, Western blotting analysis of WT and TcVP1–3×c-Myc cell lines. Anti-c-Myc antibodies detect TcVP1–3×c-Myc (expected size, 91 kDa). Anti-TbVP1 antibodies detect endogenous TcVP1 (85 kDa). F, fluorescence microscopy of TcVP1–3×c-Myc epimastigotes indicates localization of the endogenous tagged protein to acidocalcisomes. TcVP1–3×c-Myc was detected with monoclonal anti-c-Myc antibodies (green) or with polyclonal anti-TbVP1 antibodies (red). The merge shows co-localization in yellow. Differential interference contrast (DIC) images are shown in the left panel. Nucleus and kinetoplast were labeled with DAPI (blue). Bars, 10 μm.