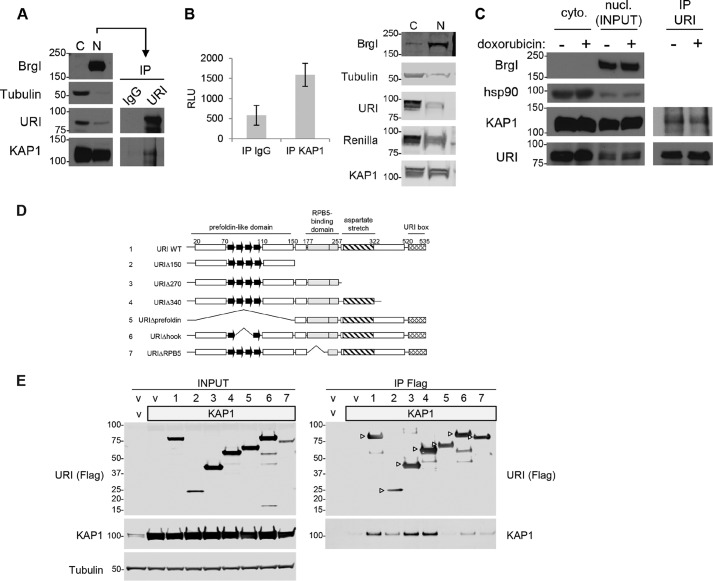
FIGURE 1.
URI interacts with KAP1. A, Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions isolated from LNCaP cells. Nuclear fractions were used for the immunoprecipitation of URI. A normal mouse IgG was used as control (IP IgG). BrgI and tubulin were used as nuclear and cytoplasmic markers, respectively (left panels). B, Renilla luciferase activity of URI tagged with Renilla luciferase co-immunoprecipitated with endogenous KAP1 from the nuclear fraction of LNCaP cells (left panel). The nuclear protein inputs are shown on the right panel. C, URI was immunoprecipitated as in A from LNCaP cells treated for 1 h with or without doxorubicin (1 μm). The data in A–C are representative of at least three independent experiments with standard deviation representing the error in B. nucl., nuclear; cyto., cytoplasmic. D, schematic of the seven URI constructs used to map domains of interaction between URI and KAP1. The known URI domains are indicated, and the numbers on top show the amino acid coordinates. E, an empty vector (v), KAP1 (gray box; 5 μg), and the various URI constructs were transfected in HEK293 cells (10 μg of total DNA was transfected in all transfections). 48 h after transfection cells were lysed. Inputs are shown in the left panel, and URI immunoprecipitated using FLAG antibodies is shown in the right panel. The immunocomplexes were analyzed by Western blot using the indicated antibodies. Arrowheads indicate the URI deletions/truncations. E is representative of three independent experiments.