FIGURE 6.
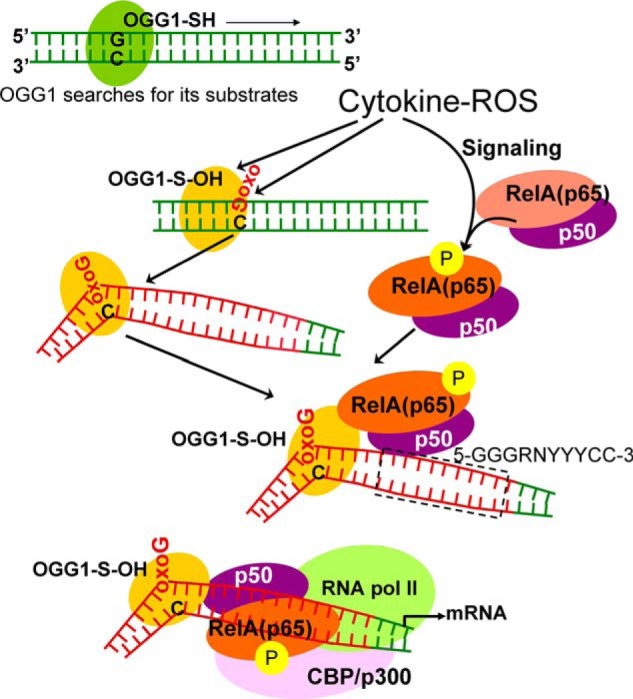
Model is shown for OGG1-mediated “homing” of NF-κB. OGG1 is a prototypic base excision repair protein, which searches for its substrates oxoG (8-oxoG, FapyG) in DNA (48). ROS-induced damage to DNA and OGG1's oxidative modification at cysteine (OGG1-SH → OGG1-S-OH) are inevitable events. OGG1-S-OH has a compromised base excision activity, although it is capable of base extrusion from DNA helix and interaction with the opposite cytosine and structural DNA modifications adjacent to its DNA footprint (39). OGG1-driven architectural DNA modification is utilized by NF-κB subunits for DNA occupancy. OGG1, 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1; oxoG, 8-oxoguanine; CBP/p300, cAMP-response element-binding protein (transcriptional co-activator); RNA pol II, RNA polymerase II; RelA(p65), 65-kDa regulatory subunit of NF-κB; p50, 50-kDa protein A DNA-binding subunit of NF-κB; 5′-GGGRNYYYCC-3′, NF-κB binding motif; G, guanine; R, purine; Y, pyrimidine; N can be any nucleotide (26).
