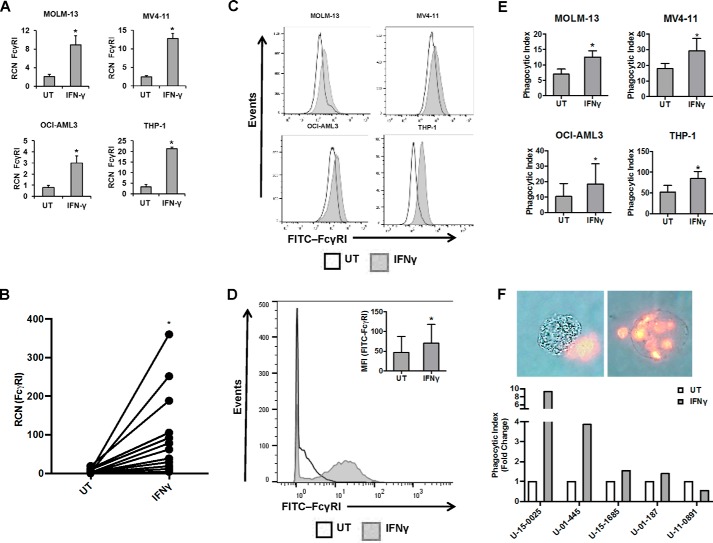
FIGURE 2.
IFNγ increases FcγRI expression and phagocytic ability in AML cells. AML cell lines MOLM-13, MV4-11, OCI-AML3, and THP-1 (n ≥ 3 separate experiments each) and primary AML apheresis samples were treated with or without 10 ng/ml IFNγ for 18 h (qPCR) or for 24 h (flow cytometry). A–D, FcγRI expression in AML cell lines (A) and primary AML apheresis samples (B, n = 12 donors) was measured by qPCR. FcγRI expression in AML cell lines (C) and primary AML apheresis samples (D, n = 3 donors, representative histogram shown; inset bar graph depicts all donors) was measured by flow cytometry. E, AML cell lines were treated with or without 10 ng/ml IFNγ for 24 h (MV4-11 cells for 48 h) and then incubated with opsonized sheep red blood cells. Phagocytosis was counted via microscopy in a blinded fashion. The phagocytic index represents the number of red blood cells ingested by 100 AML cells for each respective cell line. F, primary AML apheresis samples (n = 5 donors) were treated with or without 10 ng/ml IFNγ for 24 h and then incubated for 60 min with opsonized sheep red blood cells. Phagocytosis was counted via fluorescence microscopy in a blinded fashion. The phagocytic index represents the number of red blood cells ingested by 100 AML cells for each donor. *, p ≤ 0.05. Error bars, S.D.