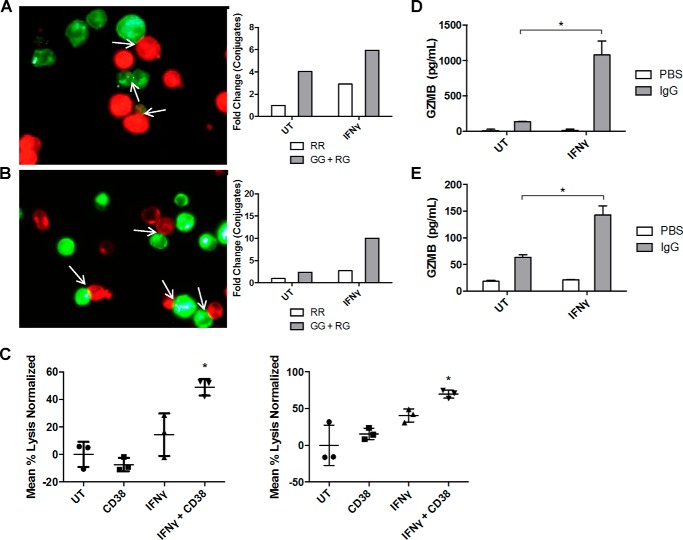
FIGURE 5.
IFNγ enhances antibody-mediated fratricide in AML cells. A and B, THP-1 cells were treated for 48 h with or without IFNγ (10 ng/ml) and then split in half to be labeled with either a red or green dye. 10 μg/ml anti-CD38 antibody was added to the green stained samples, and samples were incubated at 4 °C for 1 h. Red and green stained untreated (UT) samples were mixed, incubated for 1 h, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. 30 random images were taken by fluorescence microscopy, and conjugates were counted in a blinded fashion. The same was done for the IFNγ-treated samples. Red-red (RR) conjugates represent non-antibody-mediated conjugate formation, whereas green-green (GG) or red-green (RG) conjugates represent antibody-mediated conjugate formation. Data are represented as -fold change compared with untreated sample (n = 2 separate experiments, average shown) (A). The same procedure was repeated with MV4-11 cells (n = 2 separate experiments, average shown) (B). C, THP-1 cells (left) and MV4-11 cells (right) were treated with or without IFNγ (10 ng/ml) for 48 h, loaded with 51Cr, and labeled with anti-CD38 or IgG control antibodies. After 48 h of incubation, levels of 51Cr in supernatants were measured using a γ counter (n = 3). *, p ≤ 0.05 versus both untreated + CD38 or IFNγ + IgG. D and E, THP-1 cells were treated with or without IFNγ (10 ng/ml) for 18 h and then plated on IgG-coated 96-well plates. 24 h later, supernatants were collected, and granzyme B levels were detected via an ELISA (n = 4). *, p ≤ 0.05 versus IgG alone (D). The same procedure was repeated with MV4-11 cells (E). Error bars, S.D.