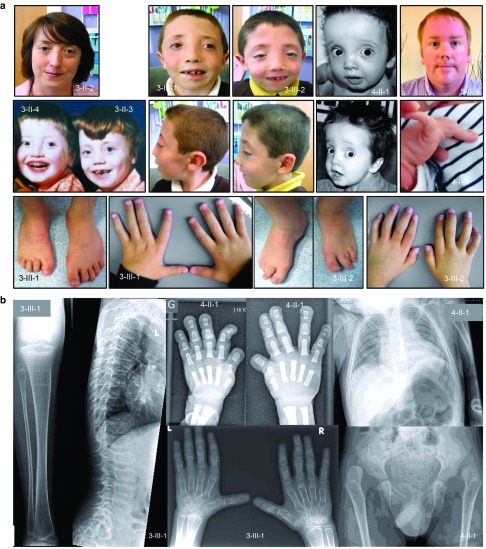
Figure 3.
Clinical features. (a) Clinical features include hypertelorism, malar flattening, down-slanting palpebral fissures (3-II-2/3/4, 3-III-1/2, and 4-II-1), proptosis (3-III-1/2), joint hypermobility (4-II-1), short spatulous fingers (3-III-1/2), and camptodactyly of fingers and toes (3-III-1/2). (b) Skeletal survey of patient 3-III-1 at age 10 years and of patient 4-II-1 at age 1.5 years. Radiograph of both hands (3-III-1) reveals asymmetry in the size of the carpal bones, with the ones on the right being larger. Overall, there is symmetric shortening and broadening of the metacarpals and phalanges that appear osteopenic with relatively thin cortices. Lateral view of the spine (3-III-1) demonstrates platyspondyly with thoracolumbar transition mild anterior tonguing. Anteroposterior view of the lower limbs (3-III-1) shows that the distal (sub)metaphyseal region of the femur is widened and the knee epiphyses are flattened. There is also mild undermodeling of the tibia with an S-shape configuration of the diaphysis. The distal tibial epiphysis is dysplastic. Skeletal radiographs of proband 4-II-1 reveal bilateral hip dislocation (treated conservatively), broadened and triangular middle phalanges, broad terminal phalanges, and a broad thorax.