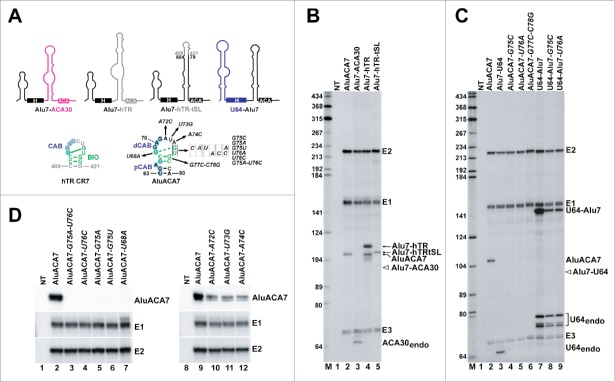
Figure 3.
Identification and functional characterization of the BIO motif in the terminal stem-loop of the 3′ hairpin of AluACA7. (A) Schematic structures of chimeric Alu7-ACA30, Alu7-hTR, Alu7-hTR-tSL and U64-Alu7 RNAs. The origin of RNA sequences is indicated by color code (black, AluACA7 RNA; pink, ACA30 snoRNA; gray, hTR; blue U64 snoRNA). The two dimensional structures of the CR7 domain of hTR and the corresponding region of AluACA7 are shown. The BIO motif nucleotides are highlighted in green and the CAB box (CAB, pCAB and dCAB) nucleotides are in blue. The continuous and dashed green lines connecting the first U and penultimate G residues of the terminal loops indicate experimentally confirmed and predicted wobble base pairs, respectively.49 Nucleotide alterations introduced into AluACA7 are indicated. (B-D) In vivo accumulation of mutant and chimeric intron-encoded AluACA RNAs processed from transiently expressed globin pre-mRNAs. Total RNAs extracted from HeLa cells transfected with the indicated pCMV-globin expression constructs (see above the lanes) were analyzed by RNase A/T1 mappings with sequence-specific antisense probes. The protected RNA fragments were analyzed on 6% sequencing gels. Positions of the spliced globin exons (E1, E2 and E3) and the processed intronic RNAs are indicated on the right. The expected positions of Alu7-ACA30 and Alu7-U64 RNAs are indicated by open arrows. NT, control mapping with RNAs from non-transfected cells. Lanes M, size markers in nucleotides.