Figure 2.
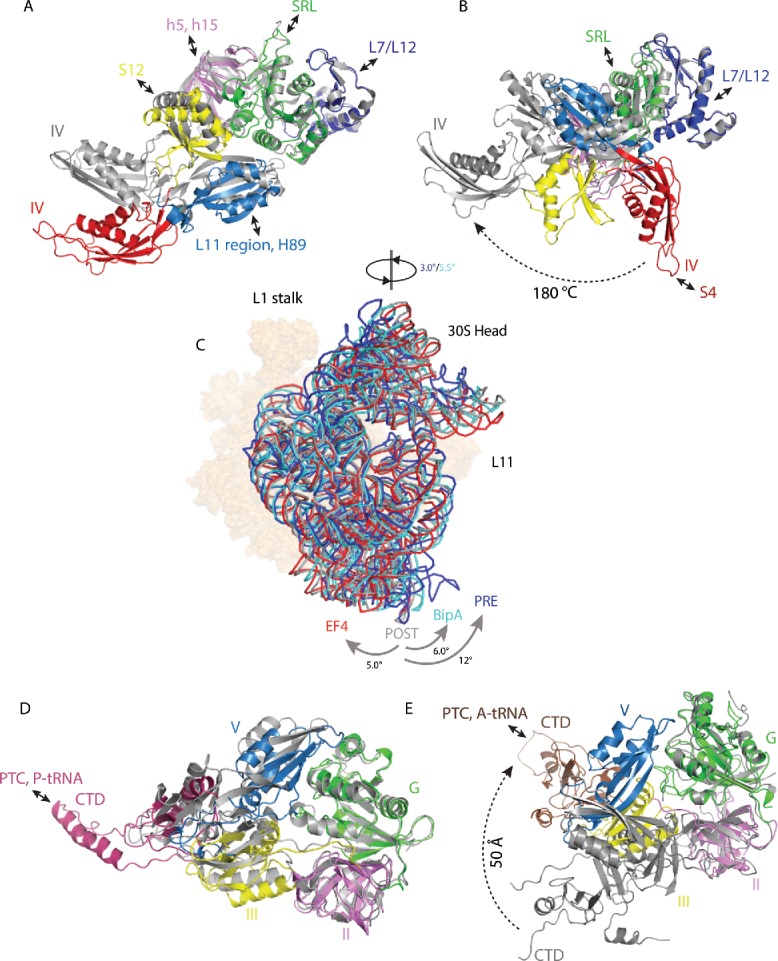
Changes in trGTPase factors and ribosome rotation upon EF-G, EF4, and BipA binding to the ribosome. (A) Comparison of isolated EF-G (PDB ID: 2BM0) with GTP form EF-G in complex with PRE state ribosome trapped by non-hydrolysable GTP analog (PDB ID: 4V90). (B) Comparison of isolated EF-G (PDB ID: 2BM0) with compact form EF-G in complex with PRE state ribosome trapped by non-hydrolysable aminoacyl-tRNA analogs (PDB ID: 4WPO). (C) Comparison of 30S body rotation and head swiveling of POST- (gray) (PDB ID: 4V5F) and PRE- (dark blue) (PDB ID: 5V7C) state ribosomes in complex with EF-G, as well as ribosomes in complex with EF4 (red) (PDB ID: 4W2E) and BipA (light blue) (PDB ID: 5A9Z). For clarity, only 16S rRNA backbone is shown for 30S subunit. 50S subunit is shown as surface in orange. (D) Comparison of isolated EF4 (PDB ID: 3CB4) with ribosome bound EF4 (PDB ID: 4W2E). (E) Comparison of isolated BipA (PDB ID: 5A9W) with ribosome bound BipA (PDB ID: 5A9Z). Ribosome bound trGTPase structures are colored as previously; isolated structures are colored gray. Interactions between trGTPase domains and ribosomal elements are highlighted with double-ended arrows.
