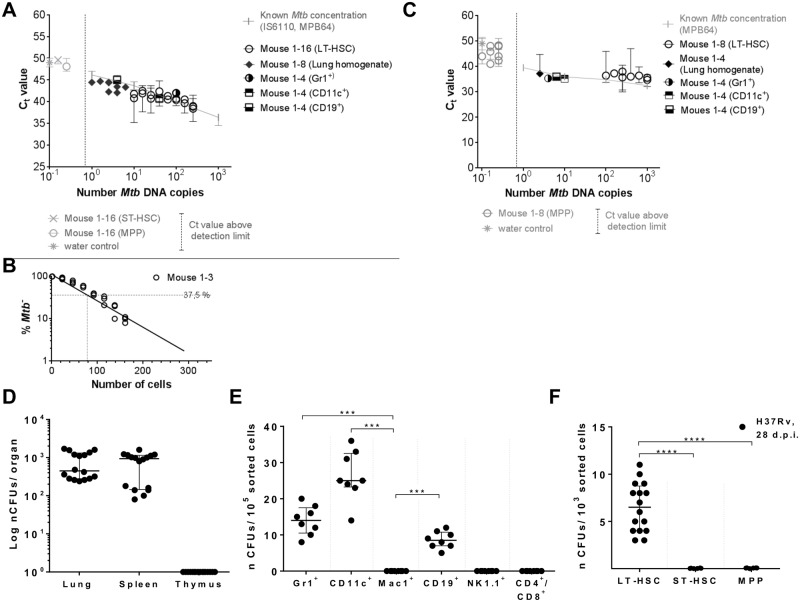
Fig 2. Detection of Mtb infection in different organs and hematopoietic cells of mice day 28 p.i. by Mtb DNA PCR and Mtb CFU.
C57BL/6 mice were infected with 105 CFUs Mtb (H37Rv). (A) Quantification of Mtb-specific DNA by real-time TaqMan PCR using probes targeting MPB64 and IS6110 (S4 Fig) on genomic DNA of 105 lung cells (n = 8), 105 Gr1+, CD11c+, CD19+, Mac1+, NK1.1+, CD4+/8+ cells (n = 4; S1C Fig), and 103 LT-pHSCs, ST-pHSCs and MPPs (n = 16; S1B Fig). (B) Quantification of Mtb-specific DNA by limiting dilutions using a single-target PCR for IS6110 (n = 3; S2B Fig). (C) Real-time SYBR green PCR using primers targeting MPB64 (n = 4–8; S4 Fig). Real-time PCRs were performed in 2 independent runs in technical triplicates and normalized to murine GAPDH. Known Mtb concentrations were used as reference. (D) CFU enumeration on Middlebrook 7H11 agar in cells of lung, spleen and thymus (n = 16). (E) CFU enumeration on Middlebrook 7H11 agar for Lin+ cell populations (n = 8). (F) CFU enumeration on Middlebrook 7H11 agar for hematopoietic progenitors (n = 16). Shown are data of 4 independent experiments. Data are shown as median + interquartile. *P ˂ 0.05, **P ˂ 0.005, ***P ˂ 0.0005, ****P ˂ 0.00005 by Mann-Whitney test.